Structural Basis of Cytotoxicity Mediated by the Type III Secretion Toxin Exou from Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
Gendrin, C., Contreras-Martel, C., Bouillot, S., Elsen, S., Lemaire, D., Skoufias, D.A., Huber, P., Attree, I., Dessen, A.(2012) PLoS Pathog 8: 2637
- PubMed: 22496657
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002637
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4AKX - PubMed Abstract:
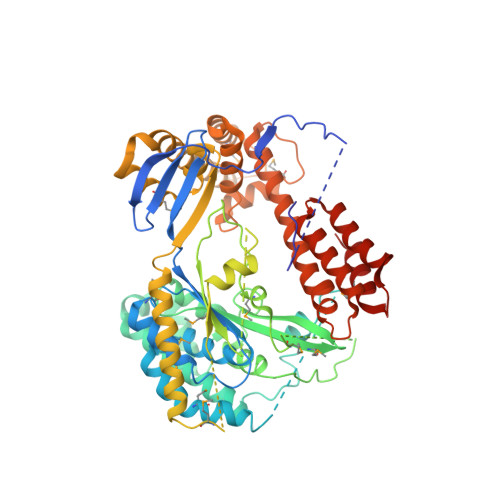
The type III secretion system (T3SS) is a complex macromolecular machinery employed by a number of Gram-negative pathogens to inject effectors directly into the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. ExoU from the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa is one of the most aggressive toxins injected by a T3SS, leading to rapid cell necrosis. Here we report the crystal structure of ExoU in complex with its chaperone, SpcU. ExoU folds into membrane-binding, bridging, and phospholipase domains. SpcU maintains the N-terminus of ExoU in an unfolded state, required for secretion. The phospholipase domain carries an embedded catalytic site whose position within ExoU does not permit direct interaction with the bilayer, which suggests that ExoU must undergo a conformational rearrangement in order to access lipids within the target membrane. The bridging domain connects catalytic domain and membrane-binding domains, the latter of which displays specificity to PI(4,5)P₂. Both transfection experiments and infection of eukaryotic cells with ExoU-secreting bacteria show that ExoU ubiquitination results in its co-localization with endosomal markers. This could reflect an attempt of the infected cell to target ExoU for degradation in order to protect itself from its aggressive cytotoxic action.
Organizational Affiliation:
Bacterial Pathogenesis Group, Institut de Biologie Structurale-IBS, Université Grenoble I, Grenoble, France.