Unraveling the Specific Regulation of the Mbd Central Pathway for the Anaerobic Degradation of 3-Methylbenzoate.
Juarez, J.F., Liu, H., Zamarro, M.T., Mcmahon, S., Liu, H., Naismith, J.H., Eberlein, C., Boll, M., Carmona, M., Diaz, E.(2015) J Biol Chem 290: 12165
- PubMed: 25795774
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.637074
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4UDS - PubMed Abstract:
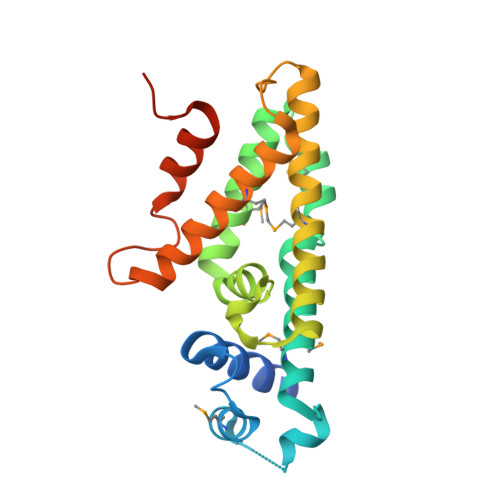
The mbd cluster encodes the anaerobic degradation of 3-methylbenzoate in the β-proteobacterium Azoarcus sp. CIB. The specific transcriptional regulation circuit that controls the expression of the mbd genes was investigated. The PO, PB 1, and P3 R promoters responsible for the expression of the mbd genes, their cognate MbdR transcriptional repressor, as well as the MbdR operator regions (ATACN10GTAT) have been characterized. The three-dimensional structure of MbdR has been solved revealing a conformation similar to that of other TetR family transcriptional regulators. The first intermediate of the catabolic pathway, i.e. 3-methylbenzoyl-CoA, was shown to act as the inducer molecule. An additional MbdR-dependent promoter, PA, which contributes to the expression of the CoA ligase that activates 3-methylbenzoate to 3-methylbenzoyl-CoA, was shown to be necessary for an efficient induction of the mbd genes. Our results suggest that the mbd cluster recruited a regulatory system based on the MbdR regulator and its target promoters to evolve a distinct central catabolic pathway that is only expressed for the anaerobic degradation of aromatic compounds that generate 3-methylbenzoyl-CoA as the central metabolite. All these results highlight the importance of the regulatory systems in the evolution and adaptation of bacteria to the anaerobic degradation of aromatic compounds.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Department of Environmental Biology, Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas-Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Ramiro de Maeztu 9, 28040 Madrid, Spain.