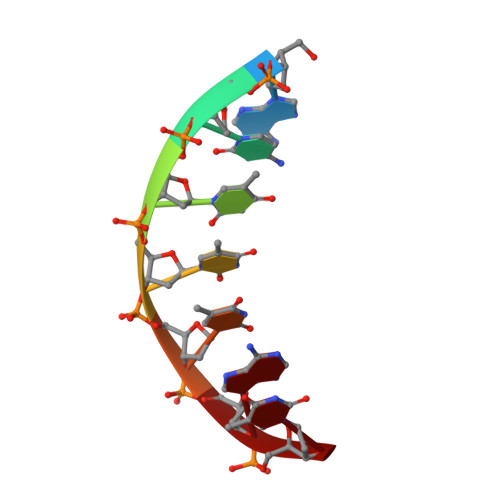
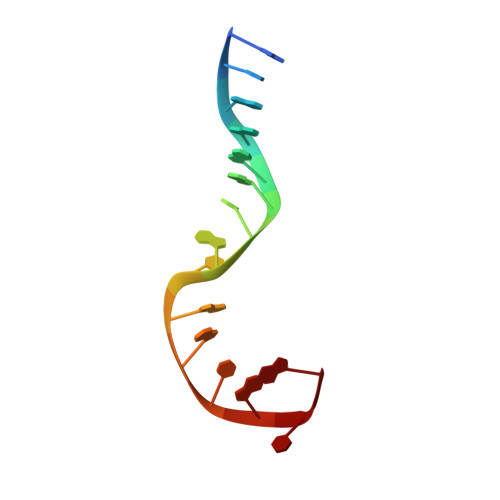
Structural basis of a histidine-DNA nicking/joining mechanism for gene transfer and promiscuous spread of antibiotic resistance.
Pluta, R., Boer, D.R., Lorenzo-Diaz, F., Russi, S., Gomez, H., Fernandez-Lopez, C., Perez-Luque, R., Orozco, M., Espinosa, M., Coll, M.(2017) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114: E6526-E6535
- PubMed: 28739894
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1702971114
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4LVI, 4LVJ, 4LVK, 4LVL, 4LVM, 5N2Q - PubMed Abstract:
Relaxases are metal-dependent nucleases that break and join DNA for the initiation and completion of conjugative bacterial gene transfer. Conjugation is the main process through which antibiotic resistance spreads among bacteria, with multidrug-resistant staphylococci and streptococci infections posing major threats to human health. The MOB V family of relaxases accounts for approximately 85% of all relaxases found in Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Here, we present six structures of the MOB V relaxase MobM from the promiscuous plasmid pMV158 in complex with several origin of transfer DNA fragments. A combined structural, biochemical, and computational approach reveals that MobM follows a previously uncharacterized histidine/metal-dependent DNA processing mechanism, which involves the formation of a covalent phosphoramidate histidine-DNA adduct for cell-to-cell transfer. We discuss how the chemical features of the high-energy phosphorus-nitrogen bond shape the dominant position of MOB V histidine relaxases among small promiscuous plasmids and their preference toward Gram-positive bacteria.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Research in Biomedicine, Barcelona Institute of Science and Technology, 08028 Barcelona, Spain.