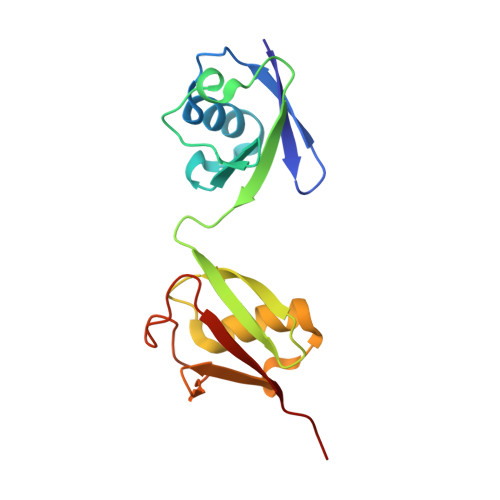
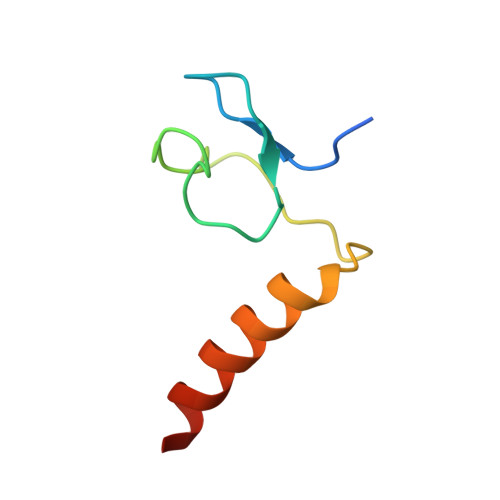
Specific recognition of linear ubiquitin chains by the Npl4 zinc finger (NZF) domain of the HOIL-1L subunit of the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex
Sato, Y., Fujita, H., Yoshikawa, A., Yamashita, M., Yamagata, A., Kaiser, S.E., Iwai, K., Fukai, S.(2011) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108: 20520-20525
- PubMed: 22139374
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1109088108
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3B08, 3B0A - PubMed Abstract:
The linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC) is a key nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway component that produces linear polyubiquitin chains. The HOIL-1L subunit of LUBAC has been shown to bind linear chains; however, detailed structural and functional analyses on the binding between LUBAC and linear chains have not been performed. In this study, we found that the Npl4 zinc finger (NZF) domain of HOIL-1L specifically binds linear polyubiquitin chains and determined the crystal structure of the HOIL-1L NZF domain in complex with linear diubiquitin at 1.7-Å resolution. The HOIL-1L NZF domain consists of a zinc-coordinating "NZF core" region and an additional α-helical "NZF tail" region. The HOIL-1L NZF core binds both the canonical Ile44-centered hydrophobic surface on the distal ubiquitin and a Phe4-centered hydrophobic patch on the proximal ubiquitin, representing a mechanism for the specific recognition of linear chains. The NZF tail binds the proximal ubiquitin to enhance the binding affinity. These recognition mechanisms were supported by the accompanying in vitro and in vivo structure-based mutagenesis experiments.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Laboratory, Life Science Division, Synchrotron Radiation Research Organization and Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biosciences, University of Tokyo, Tokyo 113-0032, Japan.