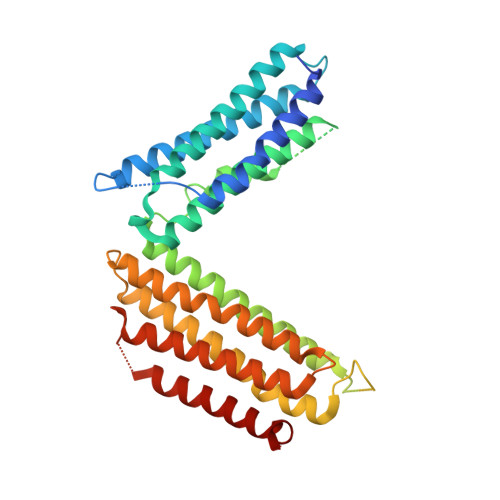
Structure of a dominant-negative helix-loop-helix transcriptional regulator suggests mechanisms of autoinhibition.
Ishii, R., Isogaya, K., Seto, A., Koinuma, D., Watanabe, Y., Arisaka, F., Yaguchi, S., Ikushima, H., Dohmae, N., Miyazono, K., Miyazawa, K., Ishitani, R., Nureki, O.(2012) EMBO J 31: 2541-2552
- PubMed: 22453338
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.77
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3AY5 - PubMed Abstract:
Helix-loop-helix (HLH) family transcription factors regulate numerous developmental and homeostatic processes. Dominant-negative HLH (dnHLH) proteins lack DNA-binding ability and capture basic HLH (bHLH) transcription factors to inhibit cellular differentiation and enhance cell proliferation and motility, thus participating in patho-physiological processes. We report the first structure of a free-standing human dnHLH protein, HHM (Human homologue of murine maternal Id-like molecule). HHM adopts a V-shaped conformation, with N-terminal and C-terminal five-helix bundles connected by the HLH region. In striking contrast to the common HLH, the HLH region in HHM is extended, with its hydrophobic dimerization interfaces embedded in the N- and C-terminal helix bundles. Biochemical and physicochemical analyses revealed that HHM exists in slow equilibrium between this V-shaped form and the partially unfolded, relaxed form. The latter form is readily available for interactions with its target bHLH transcription factors. Mutations disrupting the interactions in the V-shaped form compromised the target transcription factor specificity and accelerated myogenic cell differentiation. Therefore, the V-shaped form of HHM may represent an autoinhibited state, and the dynamic conformational equilibrium may control the target specificity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biophysics and Biochemistry, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, Japan.