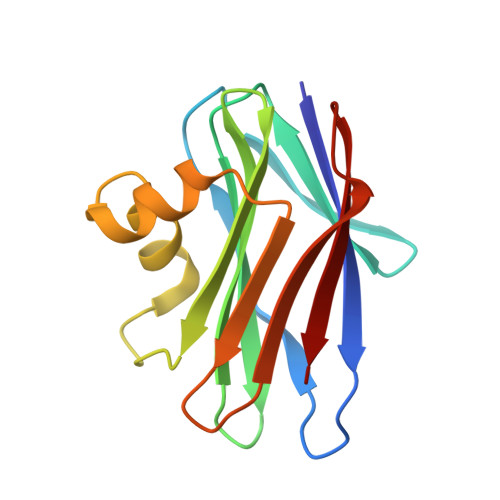
Structural Basis for the Carbohydrate Recognition of the Sclerotium rolfsii Lectin
Leonidas, D.D., Swamy, B.M., Hatzopoulos, G.N., Gonchigar, S.J., Chachadi, V.B., Inamdar, S.R., Zographos, S.E., Oikonomakos, N.G.(2007) J Mol Biol 368: 1145-1161
- PubMed: 17391699
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.02.092
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2OFC, 2OFD, 2OFE - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of a novel fungal lectin from Sclerotium rolfsii (SRL) in its free form and in complex with N-acetyl-d-galactosamine (GalNAc) and N-acetyl- d -glucosamine (GlcNAc) has been determined at 1.1 A, 2.0 A, and 1.7 A resolution, respectively. The protein structure is composed of two beta-sheets, which consist of four and six beta-strands, connected by two alpha-helices. Sequence and structural comparisons reveal that SRL is the third member of a newly identified family of fungal lectins, which includes lectins from Agaricus bisporus and Xerocomus chrysenteron that share a high degree of structural similarity and carbohydrate specificity. The data for the free SRL are the highest resolution data for any protein of this family. The crystal structures of the SRL in complex with two carbohydrates, GalNAc and GlcNAc, which differ only in the configuration of a single epimeric hydroxyl group, provide the structural basis for its carbohydrate specificity. SRL has two distinct carbohydrate-binding sites, a primary and a secondary. GalNAc binds at the primary site, whereas GlcNAc binds only at the secondary site. Thus, SRL has the ability to recognize and probably bind at the same time two different carbohydrate structures. Structural comparison to Agaricus bisporus lectin-carbohydrate complexes reveals that the primary site is also able to bind the Thomsen-Friedenreich antigen (Galbeta1-->3GalNAc-alpha- glycan structures) whereas the secondary site cannot. The features of the molecular recognition at the two sites are described in detail.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Organic and Pharmaceutical Chemistry, The National Hellenic Research Foundation, 48 Vas. Constantinou Avenue, 11635 Athens, Greece. ddl@eie.gr