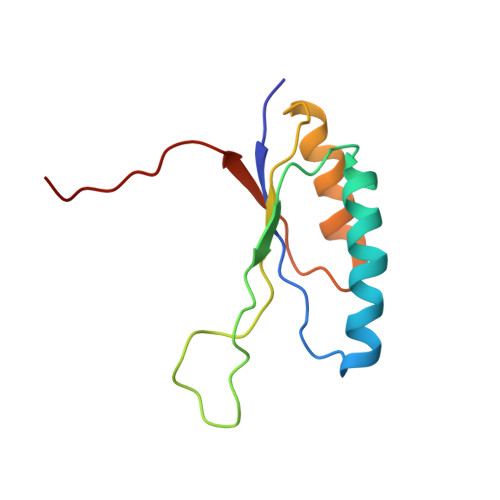
Solution structures and backbone dynamics of the ribosomal protein S6 and its permutant P(54-55)
Ohman, A., Oman, T., Oliveberg, M.(2010) Protein Sci 19: 183-189
- PubMed: 19937661
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.298
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2KJV, 2KJW - PubMed Abstract:
The ribosomal protein S6 from Thermus thermophilus has served as a model system for the study of protein folding, especially for understanding the effects of circular permutations of secondary structure elements. This study presents the structure of a permutant protein, the 96-residue P(54-55), and the structure of its 101-residue parent protein S6(wt) in solution. The data also characterizes the effects of circular permutation on the backbone dynamics of S6. Consistent with crystallographic data on S6(wt), the overall solution structures of both P(54-55) and S6(wt) show a beta-sheet of four antiparallel beta-strands with two alpha-helices packed on one side of the sheet. In clear contrast to the crystal data, however, the solution structure of S6(wt) reveals a disordered loop in the region between beta-strands 2 and 3 (Leu43-Phe60) instead of a well-ordered stretch and associated hydrophobic mini-core observed in the crystal structure. Moreover, the data for P(54-55) show that the joined wild-type N- and C-terminals form a dynamically robust stretch with a hairpin structure that complies with the in silico design. Taken together, the results explain why the loop region of the S6(wt) structure is relatively insensitive to mutational perturbations, and why P(54-55) is more stable than S6(wt): the permutant incision at Lys54-Asp55 is energetically neutral by being located in an already disordered loop whereas the new hairpin between the wild-type N- and C-termini is stabilizing.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Umeå University, Umeå SE-901 87, Sweden. anders.ohman@chem.umu.se