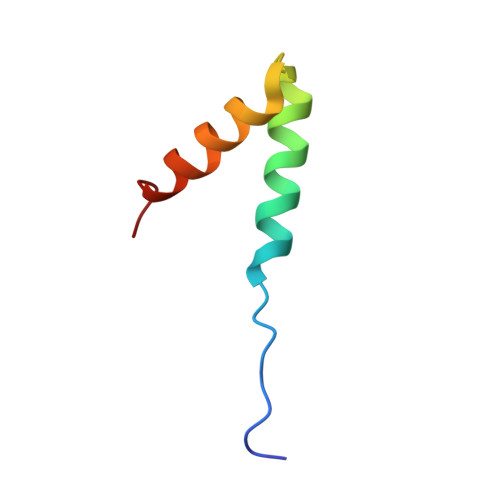
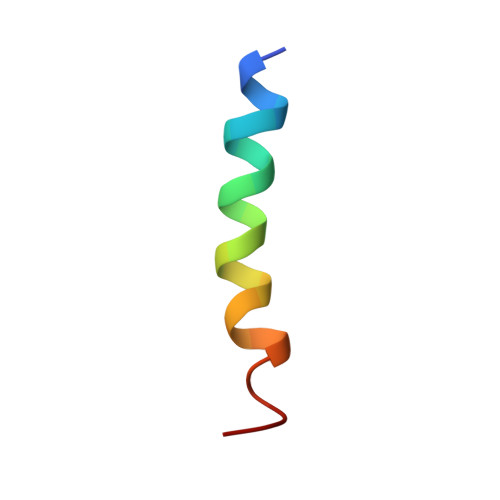
A novel mechanism of PKA anchoring revealed by solution structures of anchoring complexes.
Newlon, M.G., Roy, M., Morikis, D., Carr, D.W., Westphal, R., Scott, J.D., Jennings, P.A.(2001) EMBO J 20: 1651-1662
- PubMed: 11285229
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.7.1651
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2DRN, 2H9R - PubMed Abstract:
The specificity of intracellular signaling events is controlled, in part, by compartmentalization of protein kinases and phosphatases. The subcellular localization of these enzymes is often maintained by protein- protein interactions. A prototypic example is the compartmentalization of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) through its association with A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs). A docking and dimerization domain (D/D) located within the first 45 residues of each regulatory (R) subunit protomer forms a high affinity binding site for its anchoring partner. We now report the structures of two D/D-AKAP peptide complexes obtained by solution NMR methods, one with Ht31(493-515) and the other with AKAP79(392-413). We present the first direct structural data demonstrating the helical nature of the peptides. The structures reveal conserved hydrophobic interaction surfaces on the helical AKAP peptides and the PKA R subunit, which are responsible for mediating the high affinity association in the complexes. In a departure from the dimer-dimer interactions seen in other X-type four-helix bundle dimeric proteins, our structures reveal a novel hydrophobic groove that accommodates one AKAP per RIIalpha D/D.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093-0359, USA.