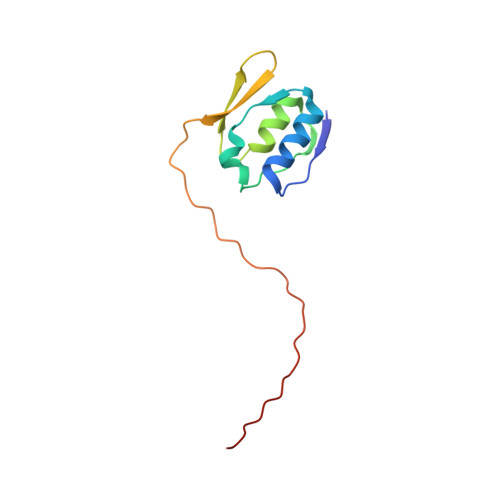
Nuclear magnetic resonance solution structure of the periplasmic signalling domain of the TonB-dependent outer membrane transporter FecA from Escherichia coli
Garcia-Herrero, A., Vogel, H.J.(2005) Mol Microbiol 58: 1226-1237
- PubMed: 16313612
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04889.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2D1U - PubMed Abstract:
Gram-negative bacteria possess outer membrane receptors that utilize energy provided by the TonB system to take up iron. Several of these receptors participate in extracytoplasmic factor (ECF) signalling through an N-terminal signalling domain that interacts with a periplasmic transmembrane anti-sigma factor protein and a cytoplasmic sigma factor protein. The structures of the intact TonB-dependent outer membrane receptor FecA from Escherichia coli and FpvA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa have recently been solved by protein crystallography; however, no electron density was detected for their periplasmic signalling domains, suggesting that it was either unfolded or flexible with respect to the remainder of the protein. Here we describe the well-defined solution structure of this domain solved by multidimensional nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The monomeric protein construct contains the 79-residue N-terminal domain as well as the next 17 residues that are part of the receptor's plug domain. These form two clearly distinct regions: a highly structured domain at the N-terminal end followed by an extended flexible tail at the C-terminal end, which includes the 'TonB-box' region, and connects it to the plug domain of the receptor. The structured region consists of two alpha-helices that are positioned side by side and are sandwiched in between two small beta-sheets. This is a novel protein fold which appears to be preserved in all the periplasmic signalling domains of bacterial TonB-dependent outer membrane receptors that are involved in ECF signalling, because the hydrophobic residues that make up the core of the protein domain are highly conserved.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Research Group, Department of Biological Sciences, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW, Calgary, Alberta, Canada T2N 1N4.