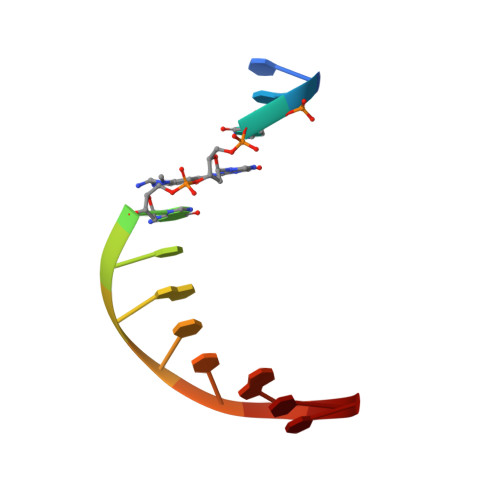
Base-Displaced Intercalated Conformation of the 2-Amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline N(2)-dG DNA Adduct Positioned at the Nonreiterated G(1) in the NarI Restriction Site.
Stavros, K.M., Hawkins, E.K., Rizzo, C.J., Stone, M.P.(2015) Chem Res Toxicol 28: 1455-1468
- PubMed: 26083477
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00140
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2N0Q - PubMed Abstract:
The conformation of an N(2)-dG adduct arising from the heterocyclic amine 2-amino-3-methylimidazo[4,5-f]quinoline (IQ), a potent food mutagen, was determined in 5'-d(C(1)T(2)C(3)X(4)G(5)C(6)G(7)C(8)C(9)A(10)T(11)C(12))-3':5'-d(G(13)A(14)T(15)G(16)G(17)C(18)G(19)C(20)C(21)G(22)A(23)G(24))-3'; X = N(2)-dG-IQ, in which the modified nucleotide X(4) corresponds to G(1) in the 5'-d(G(1)G(2)CG(3)CC)-3' NarI restriction endonuclease site. Circular dichroism (CD) revealed blue shifts relative to the unmodified duplex, consistent with adduct-induced twisting, and a hypochromic effect for the IQ absorbance in the near UV region. NMR revealed that the N(2)-dG-IQ adduct adopted a base-displaced intercalated conformation in which the modified guanine remained in the anti conformation about the glycosidic bond, the IQ moiety intercalated into the duplex, and the complementary base C(21) was displaced into the major groove. The processing of the N(2)-dG-IQ lesion by hpol η is sequence-dependent; when placed at the reiterated G(3) position, but not at the G(1) position, this lesion exhibits a propensity for frameshift replication [Choi, J. Y., et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem., 281, 25297-25306]. The structure of the N(2)-dG-IQ adduct at the nonreiterated G(1) position was compared to that of the same adduct placed at the G(3) position [Stavros, K. M., et al. (2014) Nucleic Acids Res., 42, 3450-3463]. CD indicted minimal spectral differences between the G(1) vs G(3) N(2)-dG-IQ adducts. NMR indicated that the N(2)-dG-IQ adduct exhibited similar base-displaced intercalated conformations at both the G(1) and G(3) positions. This result differed as compared to the corresponding C8-dG-IQ adducts placed at the same positions. The C8-dG-IQ adduct adopted a minor groove conformation when placed at position G(1) but a base-displaced intercalated conformation when placed at position G(3) in the NarI sequence. The present studies suggest that differences in lesion bypass by hpol η may be mediated by differences in the 3'-flanking sequences, perhaps modulating the ability to accommodate transient strand slippage intermediates.
Organizational Affiliation:
†Department of Chemistry, Center in Molecular Toxicology, Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center, and Vanderbilt Institute of Chemical Biology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee 37235-1822, United States.