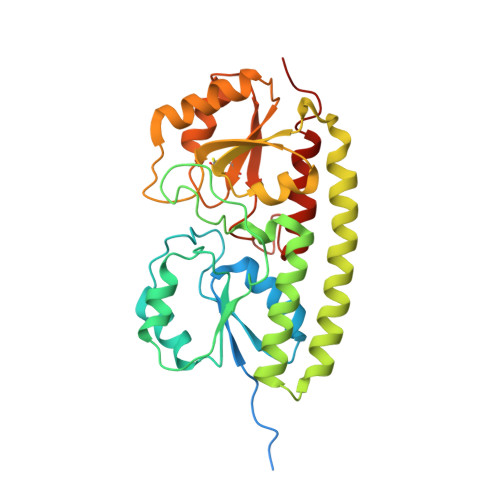
The MntC crystal structure suggests that import of Mn2+ in cyanobacteria is redox controlled.
Rukhman, V., Anati, R., Melamed-Frank, M., Adir, N.(2005) J Mol Biol 348: 961-969
- PubMed: 15843026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.03.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1XVL - PubMed Abstract:
The MntC protein is the periplasmic solute-binding protein component of the high-affinity manganese ATP-binding cassette-type transport system in the cyanobacterium Synechocytis PCC sp. 6803. We have determined the structure of recombinant MntC at 2.9 A resolution by X-ray crystallography using a combination of multi-wavelength anomalous diffraction and molecular replacement. The presence of Mn2+ in the metal ion-binding site was ascertained by use of anomalous difference electron density maps using diffraction data collected at the Mn absorption edge. The MntC protein is similar to previously determined metal ion-binding, solute-binding proteins with two globular domains connected by an extended alpha-helix. However, the metal ion-binding site is asymmetric, with two of the four ligating residues (Glu220 and Asp295) situated closer to the ion than the two histidine residues (His89 and His154). A unique characteristic of the MntC is the existence of a disulfide bond between Cys219 and Cys268. Analysis of amino acid sequences of homologous proteins shows that conservation of the cysteine residues forming the disulfide bond occurs only in cyanobacterial manganese solute-binding proteins. One of the monomers in the MntC asymmetric unit trimer is disordered significantly in the globular domain containing the disulfide bond. The electron density on the manganese ion and on the disulfide bond in this monomer indicates that reduction of this bond changes the relative position of the lower domain and of the Glu220 ligand, potentially lowering the affinity towards Mn2+. This is confirmed by reduction of the disulfide bond in vitro, showing the release of bound Mn2+. We propose that the reduction or oxidation state of the disulfide bond can alter the binding affinity of the protein towards Mn2+ and thus determine whether these ions will be transported into the cytoplasm, or be available for photosystem II biogenesis in the periplasm.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Institute of Catalysis, Science and Technology, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, Technion City, Haifa 32000, Israel.