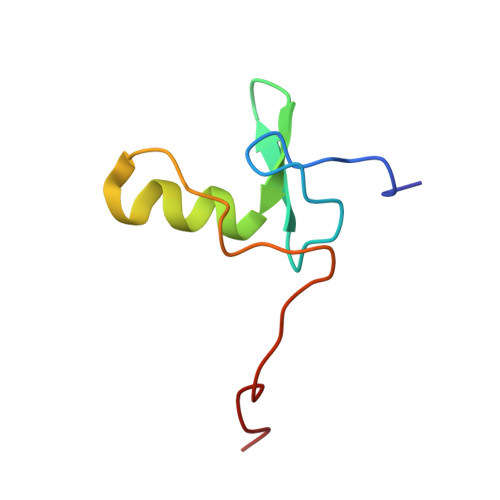
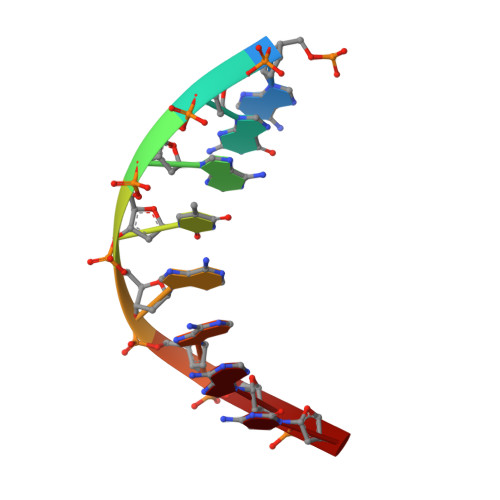
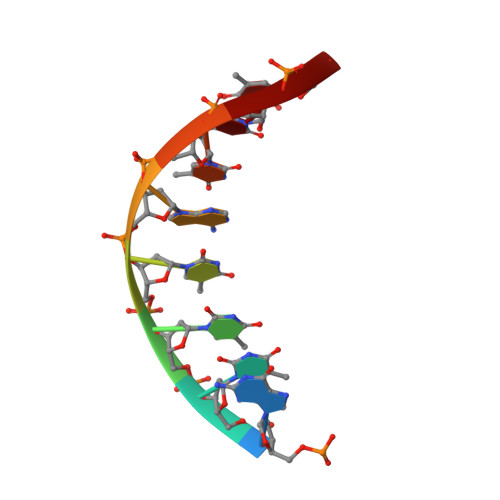
NMR structure of a specific DNA complex of Zn-containing DNA binding domain of GATA-1.
Omichinski, J.G., Clore, G.M., Schaad, O., Felsenfeld, G., Trainor, C., Appella, E., Stahl, S.J., Gronenborn, A.M.(1993) Science 261: 438-446
- PubMed: 8332909
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.8332909
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1GAT, 1GAU - PubMed Abstract:
The three-dimensional solution structure of a complex between the DNA binding domain of the chicken erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 and its cognate DNA site has been determined with multidimensional heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The DNA binding domain consists of a core which contains a zinc coordinated by four cysteines and a carboxyl-terminal tail. The core is composed of two irregular antiparallel beta sheets and an alpha helix, followed by a long loop that leads into the carboxyl-terminal tail. The amino-terminal part of the core, including the helix, is similar in structure, although not in sequence, to the amino-terminal zinc module of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain. In the other regions, the structures of these two DNA binding domains are entirely different. The DNA target site in contact with the protein spans eight base pairs. The helix and the loop connecting the two antiparallel beta sheets interact with the major groove of the DNA. The carboxyl-terminal tail, which is an essential determinant of specific binding, wraps around into the minor groove. The complex resembles a hand holding a rope with the palm and fingers representing the protein core and the thumb, the carboxyl-terminal tail. The specific interactions between GATA-1 and DNA in the major groove are mainly hydrophobic in nature, which accounts for the preponderance of thymines in the target site. A large number of interactions are observed with the phosphate backbone.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Chemical Physics, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20892.