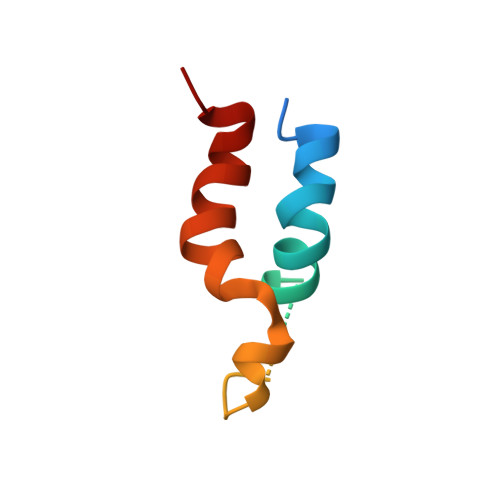
Determination of local protein structure by spin label difference 2D NMR: the region neighboring Asp61 of subunit c of the F1F0 ATP synthase.
Girvin, M.E., Fillingame, R.H.(1995) Biochemistry 34: 1635-1645
- PubMed: 7849023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00005a020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ATY - PubMed Abstract:
Purified subunit c from the H(+)-transporting F1F0 ATP synthase of Escherichia coli folds as an antiparallel pair of extended helices in a solution of chloroform-methanol-water. A similar hairpin-like folding is predicted for the native protein in the multisubunit transmembrane Fo sector of the ATP synthase. A single Cys variant (A67C) of subunit c was created and modified with a maleimido-PROXYL [[3-(maleimidomethyl)-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-1-pyrrolidinyl]oxy] spin label. Pairs of 1H 2D correlation and NOE spectra were collected with the nitroxide oxidized (paramagnetic) and reduced (diamagnetic). The pairs of spectra were subtracted, yielding difference spectra containing only cross-peaks from 1H within 15 A of the spin label. These greatly simplified spectra were easily analyzed to provide complete assignments for residues 10-25 and 52-79 of the protein, 150 NOE distance restraints, and 27 hydrogen-bonding restraints. The chemical shifts and NOE patterns observed in the derivatized mutant were virtually identical to those which were resolved in the unmodified wild-type protein, strongly suggesting that the spin label was not perturbing the protein structure. The restaints enabled us to calculate a detailed structure for this region of subunit c. The structure consisted of two gently curved helices, crossing at a slight (30 degrees) angle. The C-terminal helix was disrupted from Val60 to Ala62 near the essential Pro64. Asp61, the residue thought to undergo protonation--deprotonation with each H+ transported across the membrane, was in ver der Waals contact with Ala24. The proximity of these residues had been predicted from mutant analyses, where H+ translocation was retained on moving the Asp from position 61 to 24.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biomolecular Chemistry, University of Wisconsin Medical School, Madison 53706.