A new soaking procedure for X-ray crystallographic structural determination of protein-peptide complexes.
Ballone, A., Lau, R.A., Zweipfenning, F.P.A., Ottmann, C.(2020) Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 76: 501-507
- PubMed: 33006579
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2053230X2001122X
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6Y3M, 6Y3O, 6Y3R, 6Y3S, 6Y3V, 6Y40, 6Y44, 6Y8A, 6Y8B, 6Y8D, 6Y8E - PubMed Abstract:
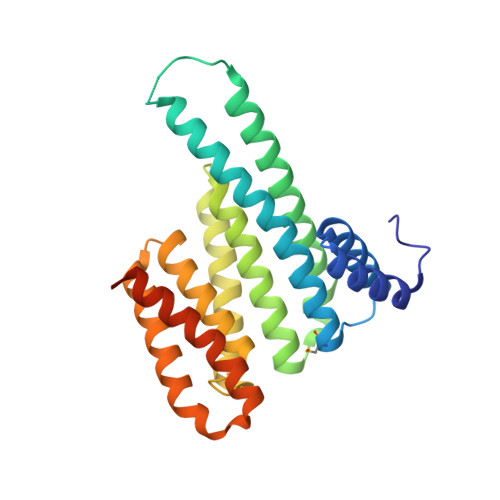
Interactions between a protein and a peptide motif of its protein partner are prevalent in nature. Often, a protein also has multiple interaction partners. X-ray protein crystallography is commonly used to examine these interactions in terms of bond distances and angles as well as to describe hotspots within protein complexes. However, the crystallization process presents a significant bottleneck in structure determination since it often requires notably time-consuming screening procedures, which involve testing a broad range of crystallization conditions via a trial-and-error approach. This difficulty is also increased as each protein-peptide complex does not necessarily crystallize under the same conditions. Here, a new co-crystallization/peptide-soaking method is presented which circumvents the need to return to the initial lengthy crystal screening and optimization processes for each consequent new complex. The 14-3-3σ protein, which has multiple interacting partners with specific peptidic motifs, was used as a case study. It was found that co-crystals of 14-3-3σ and a low-affinity peptide from one of its partners, c-Jun, could easily be soaked with another interacting peptide to quickly and easily generate new structures at high resolution. Not only does this significantly reduce the production time, but new 14-3-3-peptide structures that were previously not accessible with the 14-3-3σ isoform, despite screening hundreds of other different conditions, were now also able to be resolved. The findings achieved in this study may be considered as a supporting and practical guide to potentially enable the acceleration of the crystallization process of any protein-peptide system.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Chemical Biology, Department of Biomedical Engineering and Institute for Complex Molecular Systems, Eindhoven University of Technology, Den Dolech 2, 5612 AZ Eindhoven, The Netherlands.