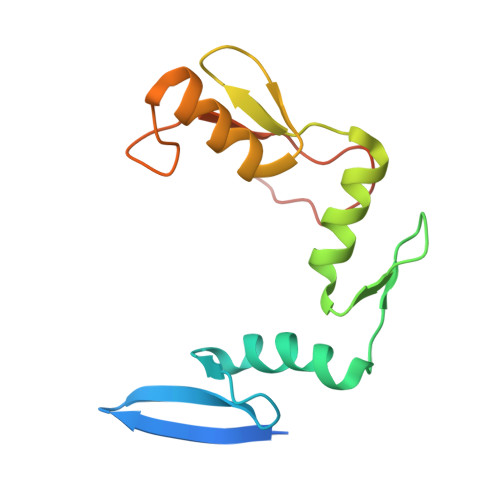
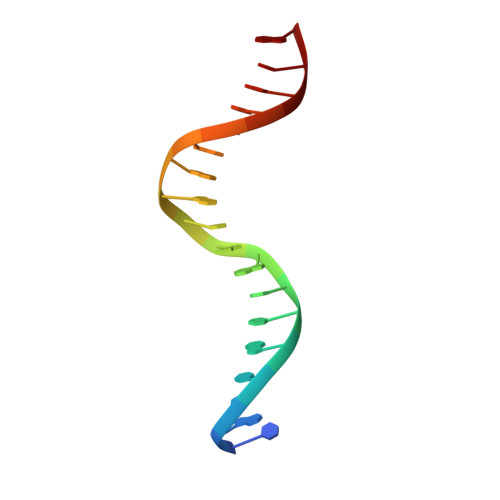
A conformational switch in the zinc finger protein Kaiso mediates differential readout of specific and methylated DNA sequences.
Nikolova, E.N., Stanfield, R.L., Dyson, H.J., Wright, P.E.(2020) Biochemistry
- PubMed: 32352758
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00253
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6DF5, 6DF8, 6DF9, 6DFA, 6DFB, 6DFC, 6V8U - PubMed Abstract:
Recognition of the epigenetic mark 5-methylcytosine (mC) at CpG sites in DNA has emerged as a novel function of many eukaryotic transcription factors (TFs). It remains unclear why the sequence specificity of these TFs differs for CpG-methylated motifs and consensus motifs. Here, we dissect the structural and dynamic basis for this differential DNA binding specificity in the human zinc finger TF Kaiso, which exhibits high affinity for two consecutive mCpG sites in variable contexts and also for a longer, sequence-specific Kaiso binding site (KBS). By integrating structural analysis and DNA binding studies with targeted protein mutagenesis and nucleotide substitutions, we identify distinct mechanisms for readout of methylated and KBS motifs by Kaiso. We show that a key glutamate residue (E535), critical for mCpG site recognition, adopts different conformations in complexes with specific and methylated DNA. These conformational differences, together with intrinsic variations in DNA flexibility and/or solvation at TpG versus mCpG sites, contribute to the different DNA affinity and sequence specificity. With methylated DNA, multiple direct contacts between E535 and the 5' mCpG site dominate the binding affinity, allowing for tolerance of different flanking DNA sequences. With KBS, Kaiso employs E535 as part of an indirect screen of the 5' flanking sequence, relying on key tyrosine-DNA interactions to stabilize an optimal DNA conformation and select against noncognate sites. These findings demonstrate how TFs use conformational adaptation and exploit variations in DNA flexibility to achieve distinct DNA readout outcomes and target a greater variety of regulatory and epigenetic sites than previously appreciated.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Integrative Structural and Computational Biology and Skaggs Institute of Chemical Biology, The Scripps Research Institute, 10550 North Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, California 92037, United States.