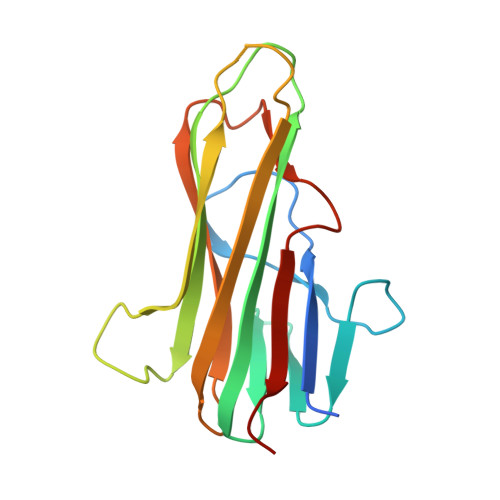
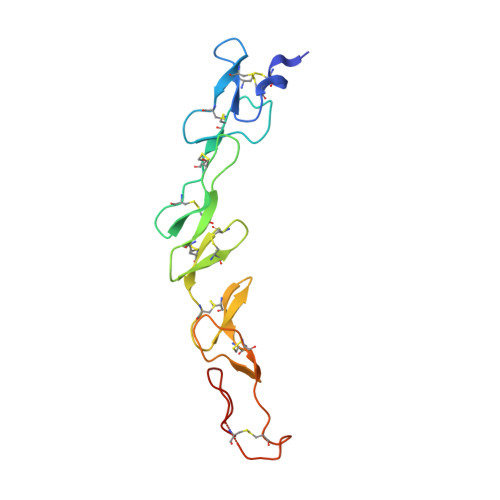
Crystal structures of the human 4-1BB receptor bound to its ligand 4-1BBL reveal covalent receptor dimerization as a potential signaling amplifier.
Bitra, A., Doukov, T., Croft, M., Zajonc, D.M.(2018) J Biol Chem 293: 9958-9969
- PubMed: 29720398
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.003176
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6CPR, 6CU0, 6D3N - PubMed Abstract:
Human (h)4-1BB (TNFRSF9 or CD137) is an inducible tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily member that interacts with its cognate ligand h4-1BBL to promote T lymphocyte activation and proliferation. h4-1BB is currently being targeted with agonists in cancer immunotherapy. Here, we determined the crystal structures of unbound h4-1BBL and both WT h4-1BB and a dimerization-deficient h4-1BB mutant (C121S) in complex with h4-1BBL at resolutions between 2.7 and 3.2 Å. We observed that the structural arrangement of 4-1BBL, both unbound and in the complex, represents the canonical bell shape as seen in other similar TNF proteins and differs from the previously reported three-bladed propeller structure of 4-1BBL. We also found that the binding site for the receptor is at the crevice formed between two protomers of h4-1BBL, but that h4-1BB interacts predominantly with only one ligand protomer. Moreover, h4-1BBL lacked the conserved tyrosine residue in the DE loop that forms canonical interactions between other TNFR family molecules and their ligands, suggesting h4-1BBL engages h4-1BB through a distinct mechanism. Of note, we discovered that h4-1BB forms a disulfide-linked dimer because of the presence of an additional cysteine residue found in its cysteine-rich domain 4 (CRD4). As a result, h4-1BB dimerization, in addition to trimerization via h4-1BBL binding, could result in cross-linking of individual ligand-receptor complexes to form a 2D network that stimulates strong h4-1BB signaling. This work provides critical insights into the structural and functional properties of both h4-1BB and h4-1BBL and reveals that covalent receptor dimerization amplifies h4-1BB signaling.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Division of Immune Regulation, La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology (LJI), La Jolla, California 92037.