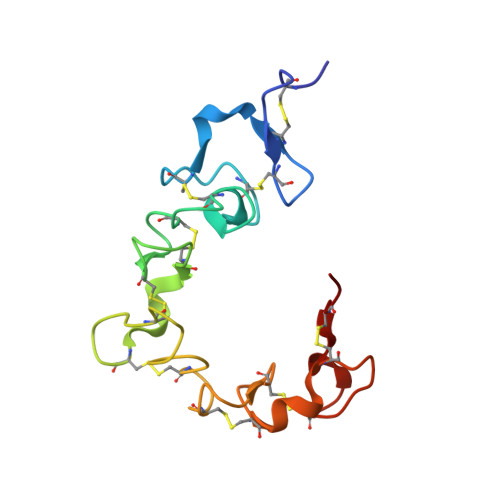
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Solution Structure of the Recombinant Fragment Containing Three Fibrin-Binding Cysteine-Rich Domains of the Very Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor.
Banerjee, K., Yakovlev, S., Gruschus, J.M., Medved, L., Tjandra, N.(2018) Biochemistry 57: 4395-4403
- PubMed: 29965730
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00349
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6BYV - PubMed Abstract:
Our previous studies revealed that interaction of fibrin with the very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) receptor plays a prominent role in transendothelial migration of leukocytes and thereby inflammation. The major goal of our subsequent studies is to establish the structural basis for this interaction. As the first step toward this goal, we localized the fibrin-binding sites within cysteine-rich (CR) domains 2-4 of the VLDL receptor. In this study, we have made a next step toward this goal by establishing the nuclear magnetic resonance solution structure of the recombinant VLDLR(2-4) fragment containing all three fibrin-binding CR domains of this receptor. The structure revealed that all three CR domains have a similar general fold. Each domain contains a calcium-binding loop, and the loop in the CR3 domain has a unique conformation relative to the other two. Domains CR2 and CR3 interact with each other, while CR4 is flexible relative to the other two domains. In addition, analysis of the electrostatic potential surface of VLDLR(2-4) revealed extended negatively charged regions in each of its CR domains. The presence of these regions suggests that they may interact with three positively charged clusters of the fibrin βN domain whose involvement in interaction with the VLDL receptor was demonstrated earlier. Altogether, these findings provide a solid background for our next step toward establishing the structural basis for fibrin-VLDL receptor interaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Molecular Biophysics, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute , National Institutes of Health , Bethesda , Maryland 20892 , United States.