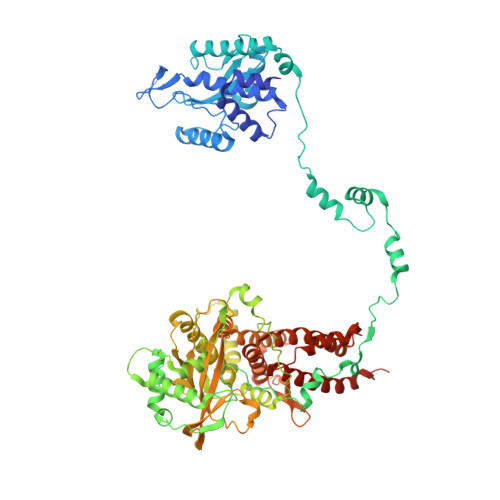
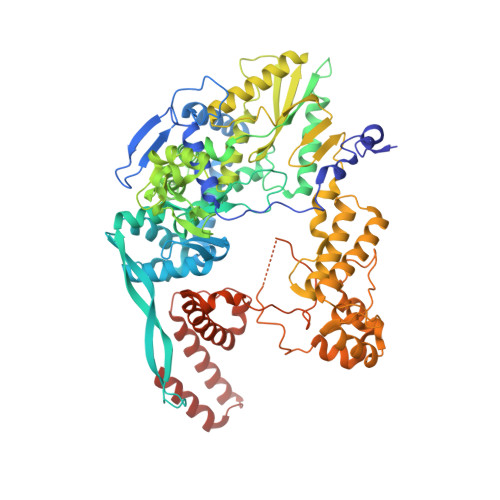
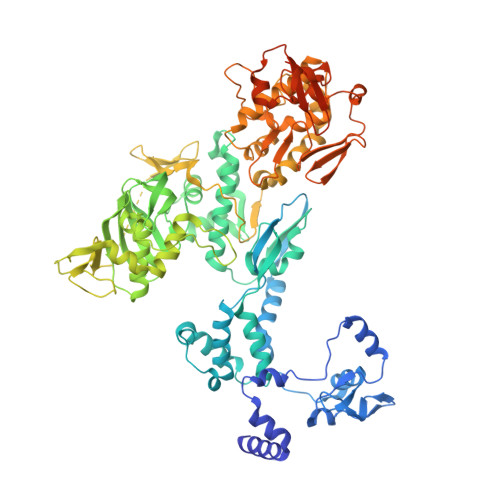
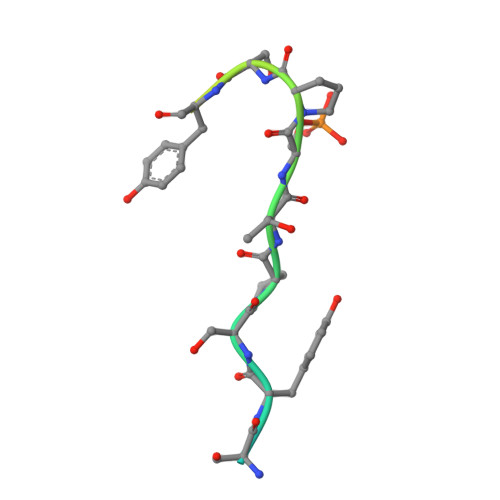
Structural basis of an essential interaction between influenza polymerase and Pol II CTD.
Lukarska, M., Fournier, G., Pflug, A., Resa-Infante, P., Reich, S., Naffakh, N., Cusack, S.(2017) Nature 541: 117-121
- PubMed: 28002402
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20594
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5M3H, 5M3J - PubMed Abstract:
The heterotrimeric influenza polymerase (FluPol), comprising subunits PA, PB1 and PB2, binds to the conserved 5' and 3' termini (the 'promoter') of each of the eight single-stranded viral RNA (vRNA) genome segments and performs both transcription and replication of vRNA in the infected cell nucleus. To transcribe viral mRNAs, FluPol associates with cellular RNA polymerase II (Pol II), which enables it to take 5'-capped primers from nascent Pol II transcripts. Here we present a co-crystal structure of bat influenza A polymerase bound to a Pol II C-terminal domain (CTD) peptide mimic, which shows two distinct phosphoserine-5 (SeP5)-binding sites in the polymerase PA subunit, accommodating four CTD heptad repeats overall. Mutagenesis of the SeP5-contacting basic residues (PA K289, R454, K635 and R638) weakens CTD repeat binding in vitro without affecting the intrinsic cap-primed (transcription) or unprimed (replication) RNA synthesis activity of recombinant polymerase, whereas in cell-based minigenome assays the same mutations substantially reduce overall polymerase activity. Only recombinant viruses with a single mutation in one of the SeP5-binding sites can be rescued, but these viruses are severely attenuated and genetically unstable. Several previously described mutants that modulate virulence can be rationalized by our results, including a second site mutation (PA(C453R)) that enables the highly attenuated mutant virus (PA(R638A)) to revert to near wild-type infectivity. We conclude that direct binding of FluPol to the SeP5 Pol II CTD is fine-tuned to allow efficient viral transcription and propose that the CTD-binding site on FluPol could be targeted for antiviral drug development.
Organizational Affiliation:
European Molecular Biology Laboratory, Grenoble Outstation, 71 Avenue des Martyrs, CS 90181, 38042 Grenoble Cedex 9, France.