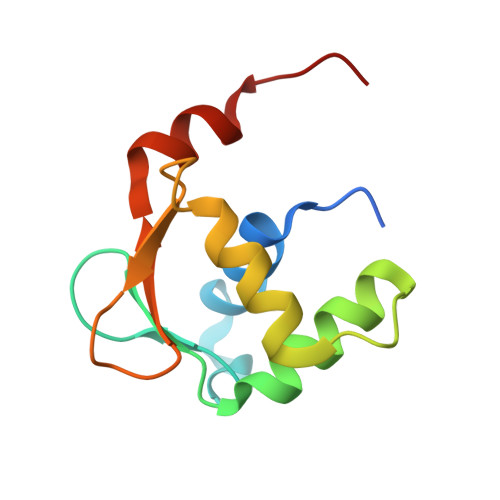
Structures of mithramycin analogues bound to DNA and implications for targeting transcription factor FLI1.
Hou, C., Weidenbach, S., Cano, K.E., Wang, Z., Mitra, P., Ivanov, D.N., Rohr, J., Tsodikov, O.V.(2016) Nucleic Acids Res 44: 8990-9004
- PubMed: 27587584
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw761
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5JVT, 5JVW, 5JW0, 5JW2 - PubMed Abstract:
Transcription factors have been considered undruggable, but this paradigm has been recently challenged. DNA binding natural product mithramycin (MTM) is a potent antagonist of oncogenic transcription factor EWS-FLI1. Structural details of MTM recognition of DNA, including the FLI1 binding sequence GGA(A/T), are needed to understand how MTM interferes with EWS-FLI1. We report a crystal structure of an MTM analogue MTM SA-Trp bound to a DNA oligomer containing a site GGCC, and two structures of a novel analogue MTM SA-Phe in complex with DNA. MTM SA-Phe is bound to sites AGGG and GGGT on one DNA, and to AGGG and GGGA(T) (a FLI1 binding site) on the other, revealing how MTM recognizes different DNA sequences. Unexpectedly, at sub-micromolar concentrations MTMs stabilize FLI1-DNA complex on GGAA repeats, which are critical for the oncogenic function of EWS-FLI1. We also directly demonstrate by nuclear magnetic resonance formation of a ternary FLI1-DNA-MTM complex on a single GGAA FLI1/MTM binding site. These biochemical and structural data and a new FLI1-DNA structure suggest that MTM binds the minor groove and perturbs FLI1 bound nearby in the major groove. This ternary complex model may lead to development of novel MTM analogues that selectively target EWS-FLI1 or other oncogenic transcription factors, as anti-cancer therapeutics.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40536, USA.