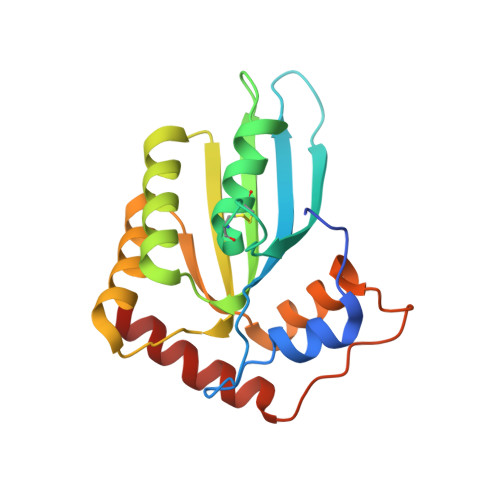
Structural Insights into HIV-1 Vif-APOBEC3F Interaction.
Nakashima, M., Ode, H., Kawamura, T., Kitamura, S., Naganawa, Y., Awazu, H., Tsuzuki, S., Matsuoka, K., Nemoto, M., Hachiya, A., Sugiura, W., Yokomaku, Y., Watanabe, N., Iwatani, Y.(2015) J Virol 90: 1034-1047
- PubMed: 26537685
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02369-15
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3WUS - PubMed Abstract:
The HIV-1 Vif protein inactivates the cellular antiviral cytidine deaminase APOBEC3F (A3F) in virus-infected cells by specifically targeting it for proteasomal degradation. Several studies identified Vif sequence motifs involved in A3F interaction, whereas a Vif-binding A3F interface was proposed based on our analysis of highly similar APOBEC3C (A3C). However, the structural mechanism of specific Vif-A3F recognition is still poorly understood. Here we report structural features of interaction interfaces for both HIV-1 Vif and A3F molecules. Alanine-scanning analysis of Vif revealed that six residues located within the conserved Vif F1-, F2-, and F3-box motifs are essential for both A3C and A3F degradation, and an additional four residues are uniquely required for A3F degradation. Modeling of the Vif structure on an HIV-1 Vif crystal structure revealed that three discontinuous flexible loops of Vif F1-, F2-, and F3-box motifs sterically cluster to form a flexible A3F interaction interface, which represents hydrophobic and positively charged surfaces. We found that the basic Vif interface patch (R17, E171, and R173) involved in the interactions with A3C and A3F differs. Furthermore, our crystal structure determination and extensive mutational analysis of the A3F C-terminal domain demonstrated that the A3F interface includes a unique acidic stretch (L291, A292, R293, and E324) crucial for Vif interaction, suggesting additional electrostatic complementarity to the Vif interface compared with the A3C interface. Taken together, these findings provide structural insights into the A3F-Vif interaction mechanism, which will provide an important basis for development of novel anti-HIV-1 drugs using cellular cytidine deaminases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Clinical Research Center, National Hospital Organization Nagoya Medical Center, Nagoya, Aichi, Japan Department of Biotechnology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Engineering, Nagoya, Aichi, Japan.