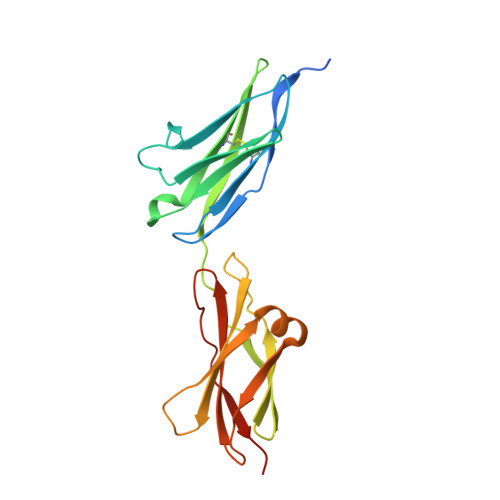
Structure and mutagenesis of neural cell adhesion molecule domains: evidence for flexibility in the placement of polysialic acid attachment sites
Foley, D.A., Swartzentruber, K.G., Lavie, A., Colley, K.J.(2010) J Biol Chem 285: 27360-27371
- PubMed: 20573953
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.140038
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3MTR - PubMed Abstract:
The addition of alpha2,8-polysialic acid to the N-glycans of the neural cell adhesion molecule, NCAM, is critical for brain development and plays roles in synaptic plasticity, learning and memory, neuronal regeneration, and the growth and invasiveness of cancer cells. Our previous work indicates that the polysialylation of two N-glycans located on the fifth immunoglobulin domain (Ig5) of NCAM requires the presence of specific sequences in the adjacent fibronectin type III repeat (FN1). To understand the relationship of these two domains, we have solved the crystal structure of the NCAM Ig5-FN1 tandem. Unexpectedly, the structure reveals that the sites of Ig5 polysialylation are on the opposite face from the FN1 residues previously found to be critical for N-glycan polysialylation, suggesting that the Ig5-FN1 domain relationship may be flexible and/or that there is flexibility in the placement of Ig5 glycosylation sites for polysialylation. To test the latter possibility, new Ig5 glycosylation sites were engineered and their polysialylation tested. We observed some flexibility in glycosylation site location for polysialylation and demonstrate that the lack of polysialylation of a glycan attached to Asn-423 may be in part related to a lack of terminal processing. The data also suggest that, although the polysialyltransferases do not require the Ig5 domain for NCAM recognition, their ability to engage with this domain is necessary for polysialylation to occur on Ig5 N-glycans.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago, Illinois 60607.