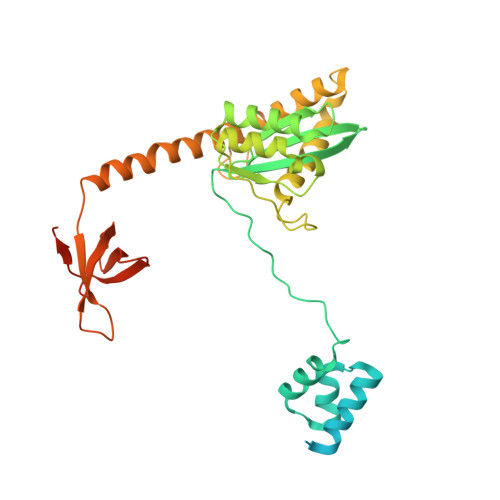
A Peptide Derived from Lens Epithelium-Derived Growth Factor Stimulates HIV-1 DNA Integration and Facilitates Intasome Structural Studies.
Li, M., Chen, X., Wang, H., Jurado, K.A., Engelman, A.N., Craigie, R.(2020) J Mol Biol 432: 2055-2066
- PubMed: 32061936
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2020.01.040
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6U8Q, 6VDK - PubMed Abstract:
The low solubility and aggregation properties of HIV-1 integrase (IN) are major obstacles for biochemical and structural studies. The lens epithelium-derived growth factor (LEDGF) is a cellular factor that binds IN and tethers preintegration complexes to chromatin before integration. The LEDGF also stimulates HIV-1 IN DNA strand transfer activity and improves its solubility in vitro. We show that these properties are conferred by a short peptide spanning residues 178 to 197 of the LEDGF that encompasses its AT-hook DNA-binding elements. The peptide stimulates HIV-1 IN activity both in trans and in cis. Fusion of the peptide to either the N- or C-terminus of IN results in maximal stimulation of concerted integration activity and greatly improves the solubility of the protein and nucleoprotein complexes of IN with viral DNA ends (intasomes). High-resolution structures of HIV-1 intasomes are required to understand the mechanism of IN strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs), which are front-line drugs for the treatment of HIV-1, and how the virus can develop resistance to INSTIs. We have previously determined the structure of the HIV-1 strand transfer complex intasome. The improved biophysical properties of intasomes assembled with LEDGF peptide fusion IN have enabled us to determine the structure of the cleaved synaptic complex intasome, which is the direct target of INSTIs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Molecular Biology, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, USA.