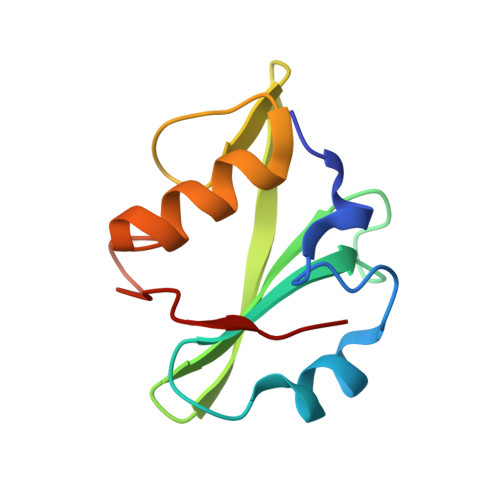
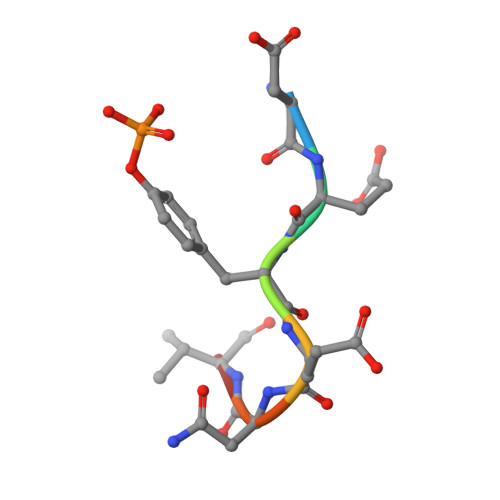
High-resolution structural analysis shows how different crystallographic environments can induce alternative modes of binding of a phosphotyrosine peptide to the SH2 domain of Fer tyrosine kinase.
Matsuura, Y.(2019) Protein Sci 28: 2011-2019
- PubMed: 31441171
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3713
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6KC4 - PubMed Abstract:
Fes and Fes-related (Fer) protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs) comprise a subfamily of nonreceptor tyrosine kinases characterized by a unique multidomain structure composed of an N-terminal Fer/CIP4 homology-Bin/Amphiphysin/Rvs (F-BAR) domain, a central Src homology 2 (SH2) domain, and a C-terminal PTK domain. Fer is ubiquitously expressed, and upregulation of Fer has been implicated in various human cancers. The PTK activity of Fes has been shown to be positively regulated by the binding of phosphotyrosine-containing ligands to the SH2 domain. Here, the X-ray crystal structure of human Fer SH2 domain bound to a phosphopeptide that has D-E-pY-E-N-V-D sequence is reported at 1.37 å resolution. The asymmetric unit (ASU) contains six Fer-phosphopeptide complexes, and the structure reveals three distinct binding modes for the same phosphopeptide. At four out of the six binding sites in the ASU, the phosphopeptide binds to Fer SH2 domain in a type I β-turn conformation, and this could be the optimal binding mode of this phosphopeptide. At the other two binding sites in the ASU, it appears that spatial proximity of neighboring SH2 domains in the crystal induces alternative modes of binding of this phosphopeptide.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Biological Science, Graduate School of Science, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan.