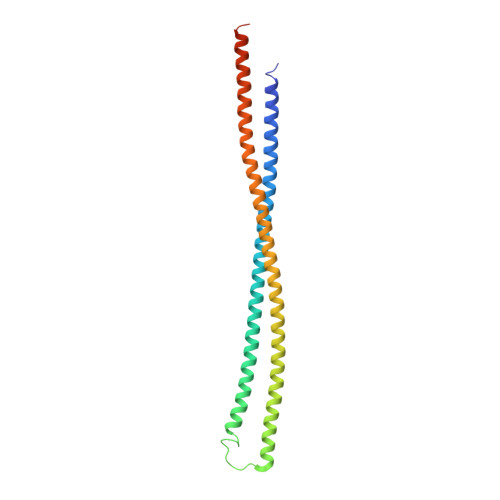
The structure of the N-terminal module of the cell wall hydrolase RipA and its role in regulating catalytic activity.
Steiner, E.M., Lyngso, J., Guy, J.E., Bourenkov, G., Lindqvist, Y., Schneider, T.R., Pedersen, J.S., Schneider, G., Schnell, R.(2018) Proteins 86: 912-923
- PubMed: 29722065
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.25523
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6EWY - PubMed Abstract:
RipA plays a vital role during cell division of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by degrading the cell wall peptidoglycan at the septum, allowing daughter cell separation. The peptidoglycan degrading activity relies on the NlpC/P60 domain, and as it is potentially harmful when deregulated, spatial and temporal control is necessary in this process. The N-terminal domain of RipA has been proposed to play an inhibitory role blocking the C-terminal NlpC/P60 domain. Accessibility of the active site cysteine residue is however not limited by the presence of the N-terminal domain, but by the lid-module of the inter-domain linker, which is situated in the peptide binding groove of the crystal structures of the catalytic domain. The 2.2 Å resolution structure of the N-terminal domain, determined by Se-SAD phasing, reveals an all-α-fold with 2 long α-helices, and shows similarity to bacterial periplasmic protein domains with scaffold-building role. Size exclusion chromatography and SAXS experiments are consistent with dimer formation of this domain in solution. The SAXS data from the periplasmic two-domain RipA construct suggest a rigid baton-like structure of the N-terminal module, with the catalytic domain connected by a 24 residue long flexible linker. This flexible linker allows for a catalytic zone, which is part of the spatiotemporal control of peptidoglycan degradation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, S-17 177, Sweden.