Definition of the R-superfamily of conotoxins: Structural convergence of helix-loop-helix peptidic scaffolds.
Moller, C., Dovell, S., Melaun, C., Mari, F.(2018) Peptides 107: 75-82
- PubMed: 30040981
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2018.06.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
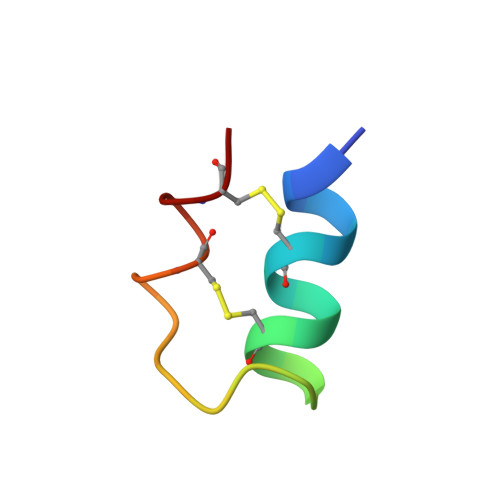
6EFE - PubMed Abstract:
The F14 conotoxins define a four-cysteine, three-loop conotoxin scaffold that produce tightly folded structures held together by two disulfide bonds with a CCCC arrangement (conotoxin framework 14). Here we describe the precursors of the F14 conotoxins from the venom of Conus anabathrum and Conus villepinii. Using transcriptomic and cDNA cloning analysis, the full-length of the precursors of flf14a and flf14b from the transcriptome of C. anabathrum revealed a unique signal sequence that defines the new conotoxin R-superfamily. Using the signal sequence as a primer, we cloned seven additional previously undescribed toxins of the R-superfamily from C. villepinii. The propeptide regions of the R-conotoxins are unusually long and with prevalent proline residues in repeating pentads which qualifies them as Pro-rich motifs (PRMs), which can be critical for protein-protein interactions or they can be cleaved to release short linear peptides that may be part of the envenomation mélange. Additionally, we determined the three-dimensional structure of vil14a by solution 1 H-NMR and found that the structure of this conotoxin displays a cysteine-stabilized α-helix-loop-helix (C s α/α) fold. The structure is well-defined over the helical regions (backbone RMSD for residues 2-13 and 17-26 is 0.63 ± 0.14 Å), with conformational flexibility in the triple Gly region of the second loop as well as the N- and C- termini. Structurally, the F14 conotoxins overlap with the C s α/α scorpion toxins and other peptidic natural products, and in spite of their different exogenomic origins, there is convergence into this scaffold from several classes of living organisms that express these peptides.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Florida Atlantic University, 777 Glades Road, Boca Raton, FL 33431-0991, USA.