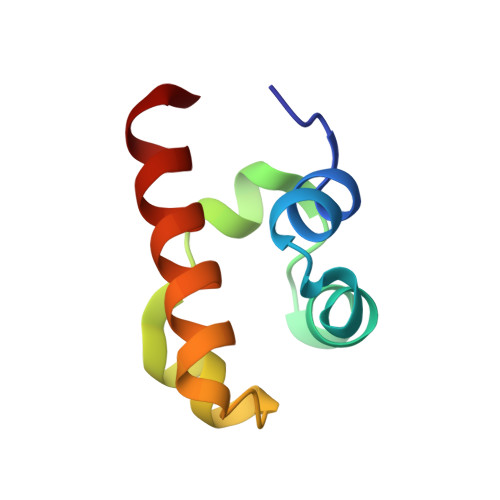
Structure of the SLy1 SAM homodimer reveals a new interface for SAM domain self-association.
Kukuk, L., Dingley, A.J., Granzin, J., Nagel-Steger, L., Thiagarajan-Rosenkranz, P., Ciupka, D., Hanel, K., Batra-Safferling, R., Pacheco, V., Stoldt, M., Pfeffer, K., Beer-Hammer, S., Willbold, D., Koenig, B.W.(2019) Sci Rep 9: 54-54
- PubMed: 30631134
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37185-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6FXF, 6G8O - PubMed Abstract:
Sterile alpha motif (SAM) domains are protein interaction modules that are involved in a diverse range of biological functions such as transcriptional and translational regulation, cellular signalling, and regulation of developmental processes. SH3 domain-containing protein expressed in lymphocytes 1 (SLy1) is involved in immune regulation and contains a SAM domain of unknown function. In this report, the structure of the SLy1 SAM domain was solved and revealed that this SAM domain forms a symmetric homodimer through a novel interface. The interface consists primarily of the two long C-terminal helices, α5 and α5', of the domains packing against each other. The dimerization is characterized by a dissociation constant in the lower micromolar range. A SLy1 SAM domain construct with an extended N-terminus containing five additional amino acids of the SLy1 sequence further increases the stability of the homodimer, making the SLy1 SAM dimer two orders of magnitude more stable than previously studied SAM homodimers, suggesting that the SLy1 SAM dimerization is of functional significance. The SLy1 SAM homodimer contains an exposed mid-loop surface on each monomer, which may provide a scaffold for mediating interactions with other SAM domain-containing proteins via a typical mid-loop-end-helix interface.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Complex Systems, Strukturbiochemie (ICS-6), Forschungszentrum Jülich, 52425, Jülich, Germany.