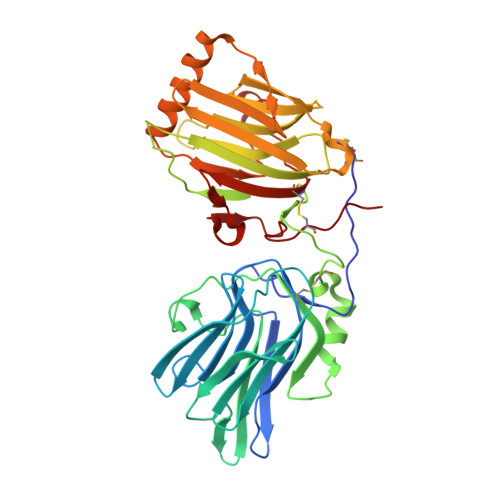
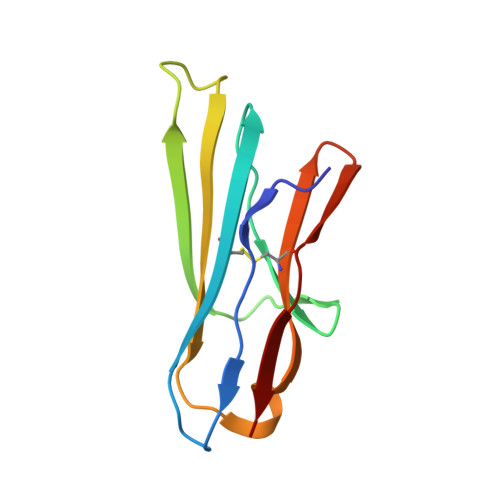
Inhibition of the GAS6/AXL pathway augments the efficacy of chemotherapies.
Kariolis, M.S., Miao, Y.R., Diep, A., Nash, S.E., Olcina, M.M., Jiang, D., Jones, D.S., Kapur, S., Mathews, I.I., Koong, A.C., Rankin, E.B., Cochran, J.R., Giaccia, A.J.(2017) J Clin Invest 127: 183-198
- PubMed: 27893463
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI85610
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5VXZ - PubMed Abstract:
The AXL receptor and its activating ligand, growth arrest-specific 6 (GAS6), are important drivers of metastasis and therapeutic resistance in human cancers. Given the critical roles that GAS6 and AXL play in refractory disease, this signaling axis represents an attractive target for therapeutic intervention. However, the strong picomolar binding affinity between GAS6 and AXL and the promiscuity of small molecule inhibitors represent important challenges faced by current anti-AXL therapeutics. Here, we have addressed these obstacles by engineering a second-generation, high-affinity AXL decoy receptor with an apparent affinity of 93 femtomolar to GAS6. Our decoy receptor, MYD1-72, profoundly inhibited disease progression in aggressive preclinical models of human cancers and induced cell killing in leukemia cells. When directly compared with the most advanced anti-AXL small molecules in the clinic, MYD1-72 achieved superior antitumor efficacy while displaying no toxicity. Moreover, we uncovered a relationship between AXL and the cellular response to DNA damage whereby abrogation of AXL signaling leads to accumulation of the DNA-damage markers γH2AX, 53BP1, and RAD51. MYD1-72 exploited this relationship, leading to improvements upon the therapeutic index of current standard-of-care chemotherapies in preclinical models of advanced pancreatic and ovarian cancer.