Structure of Main Protease from Human Coronavirus NL63: Insights for Wide Spectrum Anti-Coronavirus Drug Design.
Wang, F., Chen, C., Tan, W., Yang, K., Yang, H.(2016) Sci Rep 6: 22677-22677
- PubMed: 26948040
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22677
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5GWY - PubMed Abstract:
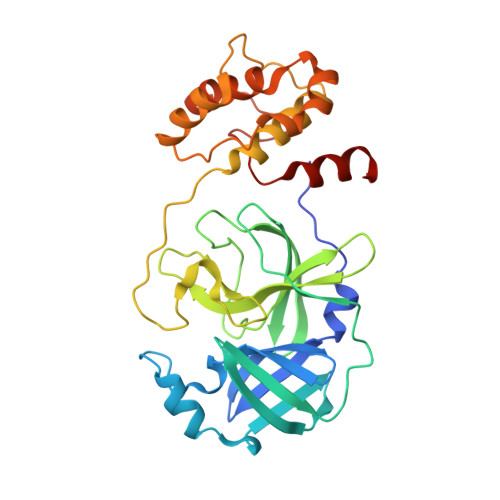
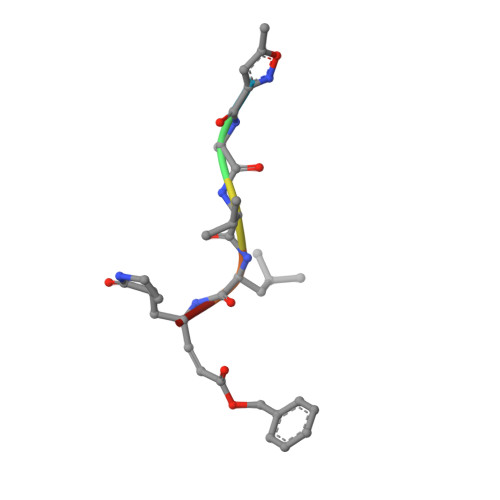
First identified in The Netherlands in 2004, human coronavirus NL63 (HCoV-NL63) was found to cause worldwide infections. Patients infected by HCoV-NL63 are typically young children with upper and lower respiratory tract infection, presenting with symptoms including croup, bronchiolitis, and pneumonia. Unfortunately, there are currently no effective antiviral therapy to contain HCoV-NL63 infection. CoV genomes encode an integral viral component, main protease (M(pro)), which is essential for viral replication through proteolytic processing of RNA replicase machinery. Due to the sequence and structural conservation among all CoVs, M(pro) has been recognized as an attractive molecular target for rational anti-CoV drug design. Here we present the crystal structure of HCoV-NL63 M(pro) in complex with a Michael acceptor inhibitor N3. Structural analysis, consistent with biochemical inhibition results, reveals the molecular mechanism of enzyme inhibition at the highly conservative substrate-recognition pocket. We show such molecular target remains unchanged across 30 clinical isolates of HCoV-NL63 strains. Through comparative study with M(pro)s from other human CoVs (including the deadly SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV) and their related zoonotic CoVs, our structure of HCoV-NL63 M(pro) provides critical insight into rational development of wide spectrum antiviral therapeutics to treat infections caused by human CoVs.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Life Sciences, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China.