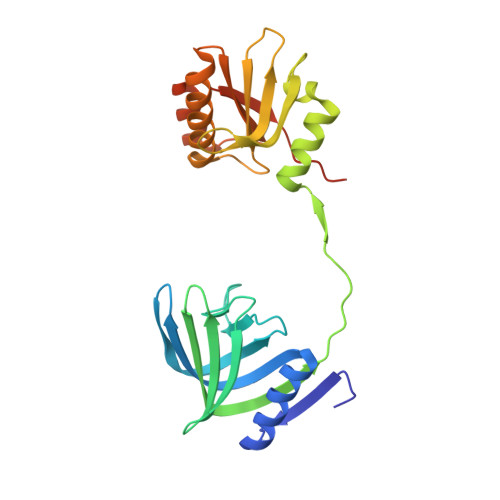
Structure of the EndoMS-DNA Complex as Mismatch Restriction Endonuclease
Nakae, S., Hijikata, A., Tsuji, T., Yonezawa, K., Kouyama, K.I., Mayanagi, K., Ishino, S., Ishino, Y., Shirai, T.(2016) Structure 24: 1960-1971
- PubMed: 27773688
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2016.09.005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5GKE, 5GKF, 5GKG, 5GKH, 5GKI, 5GKJ - PubMed Abstract:
Archaeal NucS nuclease was thought to degrade the single-stranded region of branched DNA, which contains flapped and splayed DNA. However, recent findings indicated that EndoMS, the orthologous enzyme of NucS, specifically cleaves double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) containing mismatched bases. In this study, we determined the structure of the EndoMS-DNA complex. The complex structure of the EndoMS dimer with dsDNA unexpectedly revealed that the mismatched bases were flipped out into binding sites, and the overall architecture most resembled that of restriction enzymes. The structure of the apo form was similar to the reported structure of Pyrococcus abyssi NucS, indicating that movement of the C-terminal domain from the resting state was required for activity. In addition, a model of the EndoMS-PCNA-DNA complex was preliminarily verified with electron microscopy. The structures strongly support the idea that EndoMS acts in a mismatch repair pathway.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Bioscience, Nagahama Institute of Bio-Science and Technology, Tamura 1266, Nagahama, Shiga 526-0829, Japan.