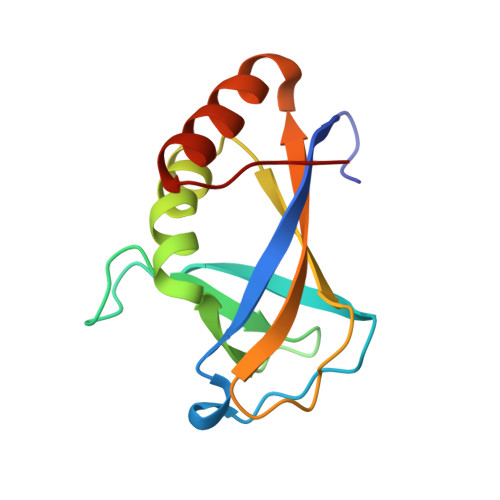
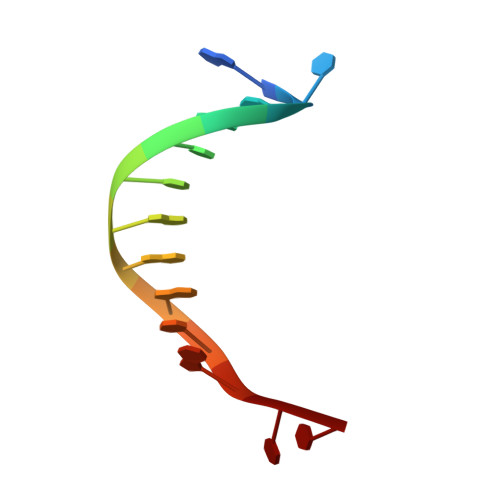
Structure of a Novel DNA-binding Domain of Helicase-like Transcription Factor (HLTF) and Its Functional Implication in DNA Damage Tolerance
Hishiki, A., Hara, K., Ikegaya, Y., Yokoyama, H., Shimizu, T., Sato, M., Hashimoto, H.(2015) J Biol Chem 290: 13215-13223
- PubMed: 25858588
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.643643
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4XZF, 4XZG - PubMed Abstract:
HLTF (helicase-like transcription factor) is a yeast RAD5 homolog found in mammals. HLTF has E3 ubiquitin ligase and DNA helicase activities, and plays a pivotal role in the template-switching pathway of DNA damage tolerance. HLTF has an N-terminal domain that has been designated the HIRAN (HIP116 and RAD5 N-terminal) domain. The HIRAN domain has been hypothesized to play a role in DNA binding; however, the structural basis of, and functional evidence for, the HIRAN domain in DNA binding has remained unclear. Here we show for the first time the crystal structure of the HIRAN domain of human HLTF in complex with DNA. The HIRAN domain is composed of six β-strands and two α-helices, forming an OB-fold structure frequently found in ssDNA-binding proteins, including in replication factor A (RPA). Interestingly, this study reveals that the HIRAN domain interacts with not only with a single-stranded DNA but also with a duplex DNA. Furthermore, the structure unexpectedly clarifies that the HIRAN domain specifically recognizes the 3'-end of DNA. These results suggest that the HIRAN domain functions as a sensor to the 3'-end of the primer strand at the stalled replication fork and that the domain facilitates fork regression. HLTF is recruited to a damaged site through the HIRAN domain at the stalled replication fork. Furthermore, our results have implications for the mechanism of template switching.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Shizuoka, 52-1 Yada, Suruga-ku, Shizuoka, Shizuoka 422-8002, Japan, the Graduate School of Medical Life Sciences, Yokohama City University, 1-7-29 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama, Kanagawa 230-0045, Japan, the Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute, La Jolla, California 92037.