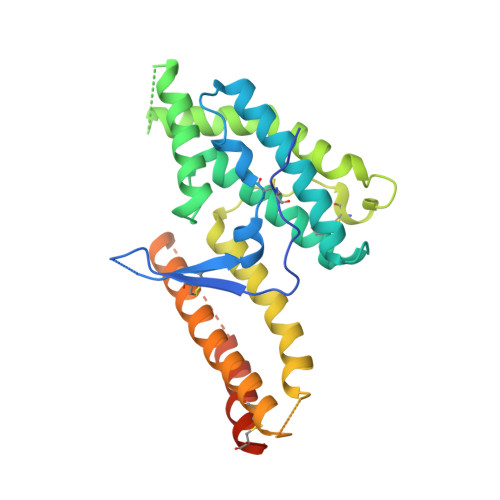
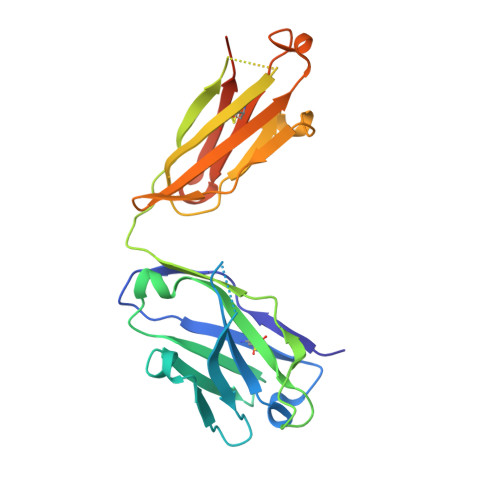
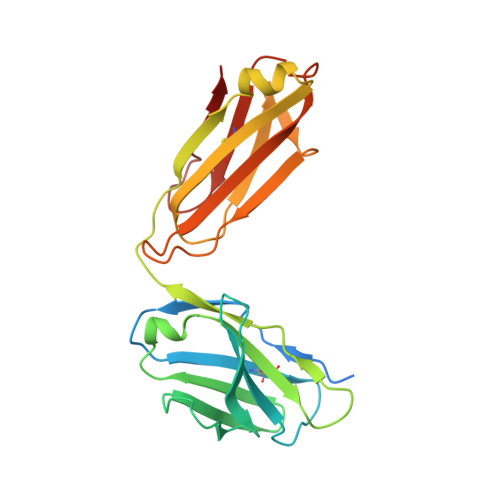
Structural and Functional Basis for Inhibition of Erythrocyte Invasion by Antibodies that Target Plasmodium falciparum EBA-175.
Chen, E., Paing, M.M., Salinas, N., Sim, B.K., Tolia, N.H.(2013) PLoS Pathog 9: e1003390-e1003390
- PubMed: 23717209
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003390
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4K2U, 4QEX - PubMed Abstract:
Disrupting erythrocyte invasion by Plasmodium falciparum is an attractive approach to combat malaria. P. falciparum EBA-175 (PfEBA-175) engages the host receptor Glycophorin A (GpA) during invasion and is a leading vaccine candidate. Antibodies that recognize PfEBA-175 can prevent parasite growth, although not all antibodies are inhibitory. Here, using x-ray crystallography, small-angle x-ray scattering and functional studies, we report the structural basis and mechanism for inhibition by two PfEBA-175 antibodies. Structures of each antibody in complex with the PfEBA-175 receptor binding domain reveal that the most potent inhibitory antibody, R217, engages critical GpA binding residues and the proposed dimer interface of PfEBA-175. A second weakly inhibitory antibody, R218, binds to an asparagine-rich surface loop. We show that the epitopes identified by structural studies are critical for antibody binding. Together, the structural and mapping studies reveal distinct mechanisms of action, with R217 directly preventing receptor binding while R218 allows for receptor binding. Using a direct receptor binding assay we show R217 directly blocks GpA engagement while R218 does not. Our studies elaborate on the complex interaction between PfEBA-175 and GpA and highlight new approaches to targeting the molecular mechanism of P. falciparum invasion of erythrocytes. The results suggest studies aiming to improve the efficacy of blood-stage vaccines, either by selecting single or combining multiple parasite antigens, should assess the antibody response to defined inhibitory epitopes as well as the response to the whole protein antigen. Finally, this work demonstrates the importance of identifying inhibitory-epitopes and avoiding decoy-epitopes in antibody-based therapies, vaccines and diagnostics.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Microbiology, Washington University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, Missouri, United States of America.