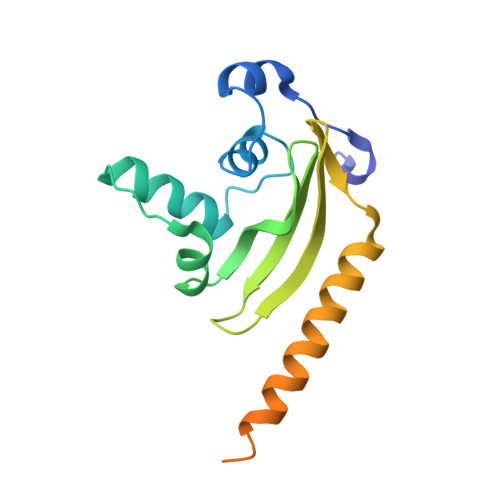
Structure of the Mediator head module.
Lariviere, L., Plaschka, C., Seizl, M., Wenzeck, L., Kurth, F., Cramer, P.(2012) Nature 492: 448-451
- PubMed: 23123849
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11670
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4H61, 4H62, 4H63 - PubMed Abstract:
Gene transcription by RNA polymerase (Pol) II requires the coactivator complex Mediator. Mediator connects transcriptional regulators and Pol II, and is linked to human disease. Mediator from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has a molecular mass of 1.4 megadaltons and comprises 25 subunits that form the head, middle, tail and kinase modules. The head module constitutes one-half of the essential Mediator core, and comprises the conserved subunits Med6, Med8, Med11, Med17, Med18, Med20 and Med22. Recent X-ray analysis of the S. cerevisiae head module at 4.3 Å resolution led to a partial architectural model with three submodules called neck, fixed jaw and moveable jaw. Here we determine de novo the crystal structure of the head module from the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe at 3.4 Å resolution. Structure solution was enabled by new structures of Med6 and the fixed jaw, and previous structures of the moveable jaw and part of the neck, and required deletion of Med20. The S. pombe head module resembles the head of a crocodile with eight distinct elements, of which at least four are mobile. The fixed jaw comprises tooth and nose domains, whereas the neck submodule contains a helical spine and one limb, with shoulder, arm and finger elements. The arm and the essential shoulder contact other parts of Mediator. The jaws and a central joint are implicated in interactions with Pol II and its carboxy-terminal domain, and the joint is required for transcription in vitro. The S. pombe head module structure leads to a revised model of the S. cerevisiae module, reveals a high conservation and flexibility, explains known mutations, and provides the basis for unravelling a central mechanism of gene regulation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Gene Center and Department of Biochemistry, Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Feodor-Lynen-Straße 25, 81377 Munich, Germany. larivier@genzentrum.lmu.de