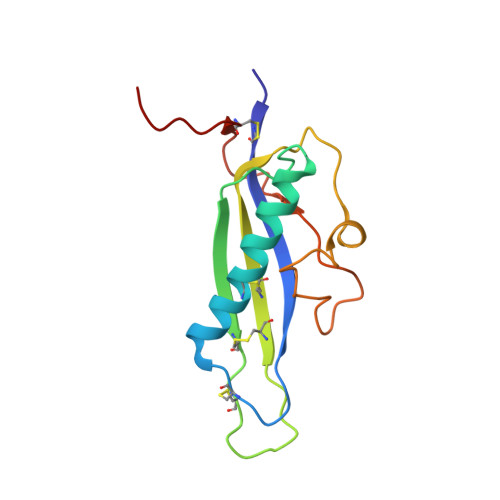
Crystal structure of the effector AvrLm4-7 of Leptosphaeria maculans reveals insights into its translocation into plant cells and recognition by resistance proteins.
Blondeau, K., Blaise, F., Graille, M., Kale, S.D., Linglin, J., Ollivier, B., Labarde, A., Lazar, N., Daverdin, G., Balesdent, M.H., Choi, D.H., Tyler, B.M., Rouxel, T., van Tilbeurgh, H., Fudal, I.(2015) Plant J 83: 610-624
- PubMed: 26082394
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12913
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4FPQ, 4FPR - PubMed Abstract:
The avirulence gene AvrLm4-7 of Leptosphaeria maculans, the causal agent of stem canker in Brassica napus (oilseed rape), confers a dual specificity of recognition by two resistance genes (Rlm4 and Rlm7) and is strongly involved in fungal fitness. In order to elucidate the biological function of AvrLm4-7 and understand the specificity of recognition by Rlm4 and Rlm7, the AvrLm4-7 protein was produced in Pichia pastoris and its crystal structure was determined. It revealed the presence of four disulfide bridges, but no close structural analogs could be identified. A short stretch of amino acids in the C terminus of the protein, (R/N)(Y/F)(R/S)E(F/W), was well-conserved among AvrLm4-7 homologs. Loss of recognition of AvrLm4-7 by Rlm4 is caused by the mutation of a single glycine to an arginine residue located in a loop of the protein. Loss of recognition by Rlm7 is governed by more complex mutational patterns, including gene loss or drastic modifications of the protein structure. Three point mutations altered residues in the well-conserved C-terminal motif or close to the glycine involved in Rlm4-mediated recognition, resulting in the loss of Rlm7-mediated recognition. Transient expression in Nicotiana benthamiana (tobacco) and particle bombardment experiments on leaves from oilseed rape suggested that AvrLm4-7 interacts with its cognate R proteins inside the plant cell, and can be translocated into plant cells in the absence of the pathogen. Translocation of AvrLm4-7 into oilseed rape leaves is likely to require the (R/N)(Y/F)(R/S)E(F/W) motif as well as an RAWG motif located in a nearby loop that together form a positively charged region.
Organizational Affiliation:
I2BC, Université Paris-Saclay, CEA, CNRS, Université Paris Sud, UMR9198, Bât 430, F-91405, Orsay, France.