Structural Determinants of an Insect {beta}-N-Acetyl-D-hexosaminidase Specialized as a Chitinolytic Enzyme
Liu, T., Zhang, H., Liu, F., Wu, Q., Shen, X., Yang, Q.(2011) J Biol Chem 286: 4049-4058
- PubMed: 21106526
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.184796
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3NSM - PubMed Abstract:
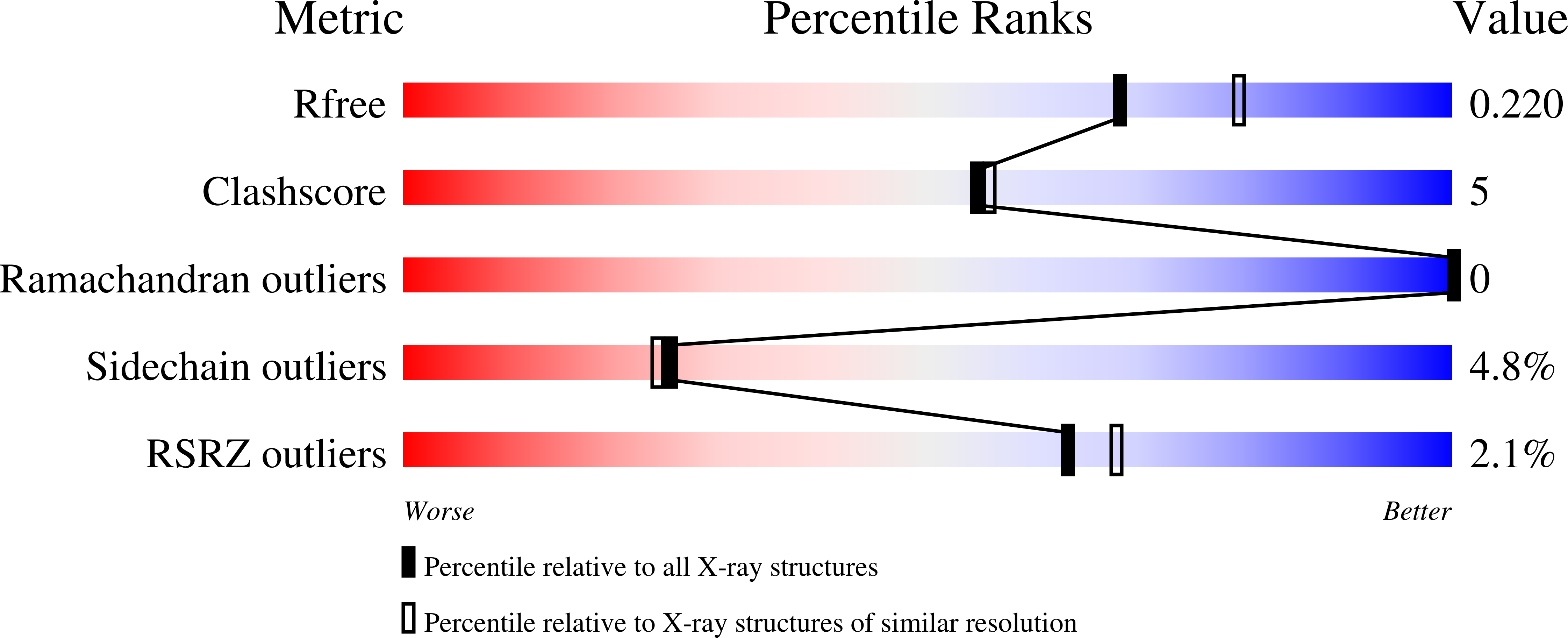
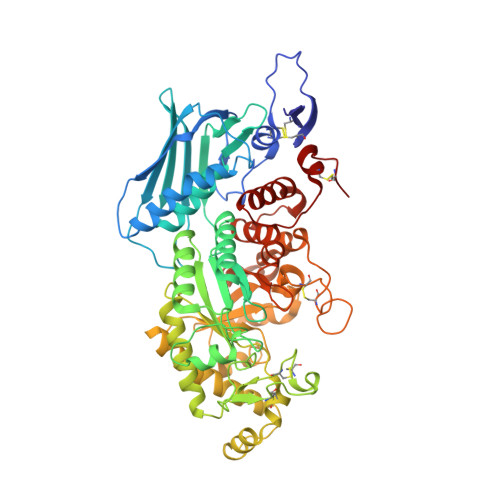
β-N-acetyl-D-hexosaminidase has been postulated to have a specialized function. However, the structural basis of this specialization is not yet established. OfHex1, the enzyme from the Asian corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis (one of the most destructive pests) has previously been reported to function merely in chitin degradation. Here the vital role of OfHex1 during the pupation of O. furnacalis was revealed by RNA interference, and the crystal structures of OfHex1 and OfHex1 complexed with TMG-chitotriomycin were determined at 2.1 Å. The mechanism of selective inhibition by TMG-chitotriomycin was related to the existence of the +1 subsite at the active pocket of OfHex1 and a key residue, Trp(490), at this site. Mutation of Trp(490) to Ala led to a 2,277-fold decrease in sensitivity toward TMG-chitotriomycin as well as an 18-fold decrease in binding affinity for the substrate (GlcNAc)(2). Although the overall topology of the catalytic domain of OfHex1 shows a high similarity with the human and bacterial enzymes, OfHex1 is distinguished from these enzymes by large conformational changes linked to an "open-close" mechanism at the entrance of the active site, which is characterized by the "lid" residue, Trp(448). Mutation of Trp(448) to Ala or Phe resulted in a more than 1,000-fold loss in enzyme activity, due mainly to the effect on k(cat). The current work has increased our understanding of the structure-function relationship of OfHex1, shedding light on the structural basis that accounts for the specialized function of β-N-acetyl-D-hexosaminidase as well as making the development of species-specific pesticides a likely reality.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024, China.