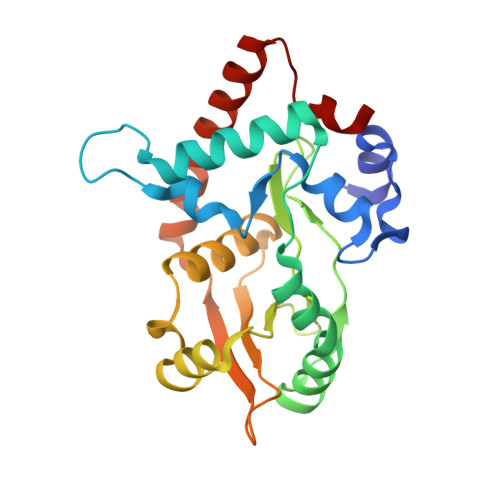
Crystal structures of {lambda} exonuclease in complex with DNA suggest an electrostatic ratchet mechanism for processivity.
Zhang, J., McCabe, K.A., Bell, C.E.(2011) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108: 11872-11877
- PubMed: 21730170
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1103467108
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3SLP, 3SM4 - PubMed Abstract:
The λ exonuclease is an ATP-independent enzyme that binds to dsDNA ends and processively digests the 5'-ended strand to form 5' mononucleotides and a long 3' overhang. The crystal structure of λ exonuclease revealed a toroidal homotrimer with a central funnel-shaped channel for tracking along the DNA, and a mechanism for processivity based on topological linkage of the trimer to the DNA was proposed. Here, we have determined the crystal structure of λ exonuclease in complex with DNA at 1.88-Å resolution. The structure reveals that the enzyme unwinds the DNA prior to cleavage, such that two nucleotides of the 5'-ended strand insert into the active site of one subunit of the trimer, while the 3'-ended strand passes through the central channel to emerge out the back of the trimer. Unwinding of the DNA is facilitated by several apolar residues, including Leu78, that wedge into the base pairs at the single/double-strand junction to form favorable hydrophobic interactions. The terminal 5' phosphate of the DNA binds to a positively charged pocket buried at the end of the active site, while the scissile phosphate bridges two active site Mg(2+) ions. Our data suggest a mechanism for processivity in which wedging of Leu78 and other apolar residues into the base pairs of the DNA restricts backward movement, whereas attraction of the 5' phosphate to the positively charged pocket drives forward movement of the enzyme along the DNA at each cycle of the reaction. Thus, processivity of λ exonuclease operates not only at the level of the trimer, but also at the level of the monomer.
Organizational Affiliation:
Ohio State Biochemistry Program and Department of Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, The Ohio State University, 1645 Neil Avenue, Columbus, OH 43210, USA.