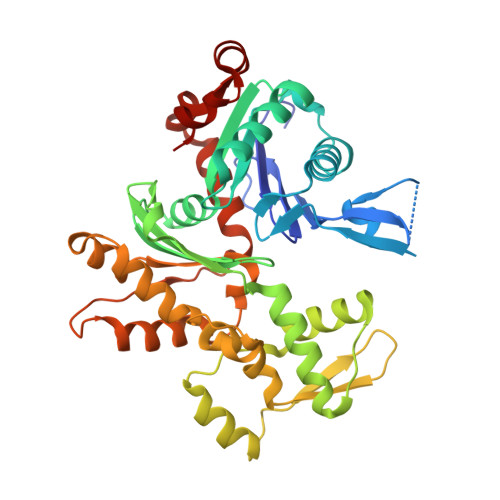
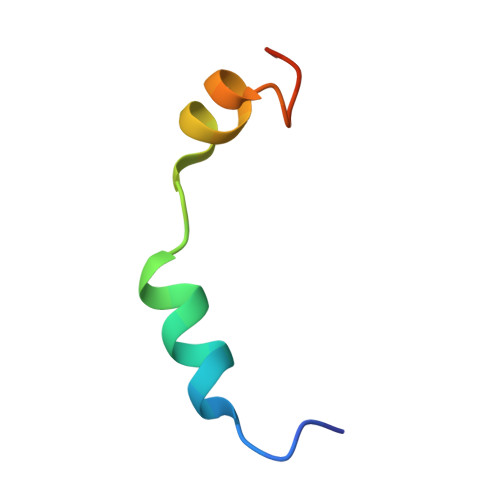
Molecular basis for G-actin binding to RPEL motifs from the serum response factor coactivator MAL.
Mouilleron, S., Guettler, S., Langer, C.A., Treisman, R., McDonald, N.Q.(2008) EMBO J 27: 3198-3208
- PubMed: 19008859
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2008.235
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2V51, 2V52 - PubMed Abstract:
Serum response factor transcriptional activity is controlled through interactions with regulatory cofactors such as the coactivator MAL/MRTF-A (myocardin-related transcription factor A). MAL is itself regulated in vivo by changes in cellular actin dynamics, which alter its interaction with G-actin. The G-actin-sensing mechanism of MAL/MRTF-A resides in its N-terminal domain, which consists of three tandem RPEL repeats. We describe the first molecular insights into RPEL function obtained from structures of two independent RPEL(MAL) peptide:G-actin complexes. Both RPEL peptides bind to the G-actin hydrophobic cleft and to subdomain 3. These RPEL(MAL):G-actin structures explain the sequence conservation defining the RPEL motif, including the invariant arginine. Characterisation of the RPEL(MAL):G-actin interaction by fluorescence anisotropy and cell reporter-based assays validates the significance of actin-binding residues for proper MAL localisation and regulation in vivo. We identify important differences in G-actin engagement between the two RPEL(MAL) structures. Comparison with other actin-binding proteins reveals an unexpected similarity to the vitamin-D-binding protein, extending the G-actin-binding protein repertoire.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Laboratory, Cancer Research UK, London Research Institute, London, UK.