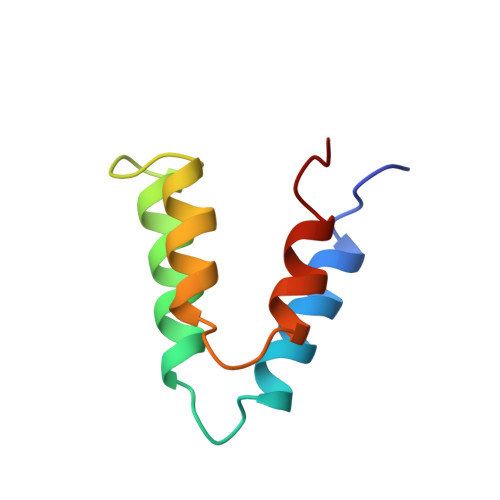
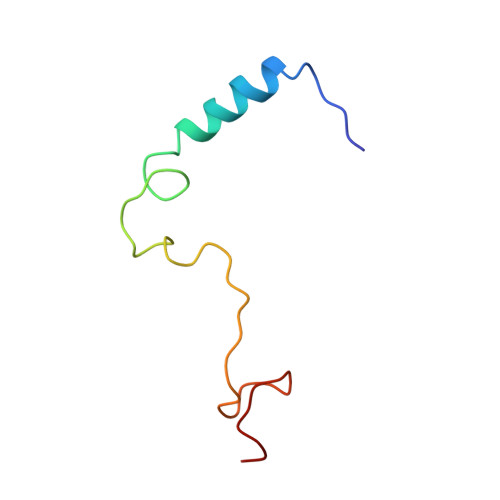
Conserved Themes in Target Recognition by the PAH1 and PAH2 Domains of the Sin3 Transcriptional Corepressor
Sahu, S.C., Swanson, K.A., Kang, R.S., Huang, K., Brubaker, K., Ratcliff, K., Radhakrishnan, I.(2007) J Mol Biol 375: 1444-1456
- PubMed: 18089292
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.11.079
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2RMR, 2RMS - PubMed Abstract:
The recruitment of chromatin-modifying coregulator complexes by transcription factors to specific sites of the genome constitutes an important step in many eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory pathways. The histone deacetylase-associated Sin3 corepressor complex is recruited by a large and diverse array of transcription factors through direct interactions with the N-terminal PAH domains of Sin3. Here, we describe the solution structures of the mSin3A PAH1 domain in the apo form and when bound to SAP25, a component of the corepressor complex. Unlike the apo-mSin3A PAH2 domain, the apo-PAH1 domain is conformationally pure and is largely, but not completely, folded. Portions of the interacting segments of both mSin3A PAH1 and SAP25 undergo folding upon complex formation. SAP25 binds through an amphipathic helix to a predominantly hydrophobic cleft on the surface of PAH1. Remarkably, the orientation of the helix is reversed compared to that adopted by NRSF, a transcription factor unrelated to SAP25, upon binding to the mSin3B PAH1 domain. The reversal in helical orientations is correlated with a reversal in the underlying PAH1-interaction motifs, echoing a theme previously described for the mSin3A PAH2 domain. The definition of these so-called type I and type II PAH1-interaction motifs has allowed us to predict the precise location of these motifs within previously experimentally characterized PAH1 binders. Finally, we explore the specificity determinants of protein-protein interactions involving the PAH1 and PAH2 domains. These studies reveal that even conservative replacements of PAH2 residues with equivalent PAH1 residues are sufficient to alter the affinity and specificity of these protein-protein interactions dramatically.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology, and Cell Biology, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208-3500, USA.