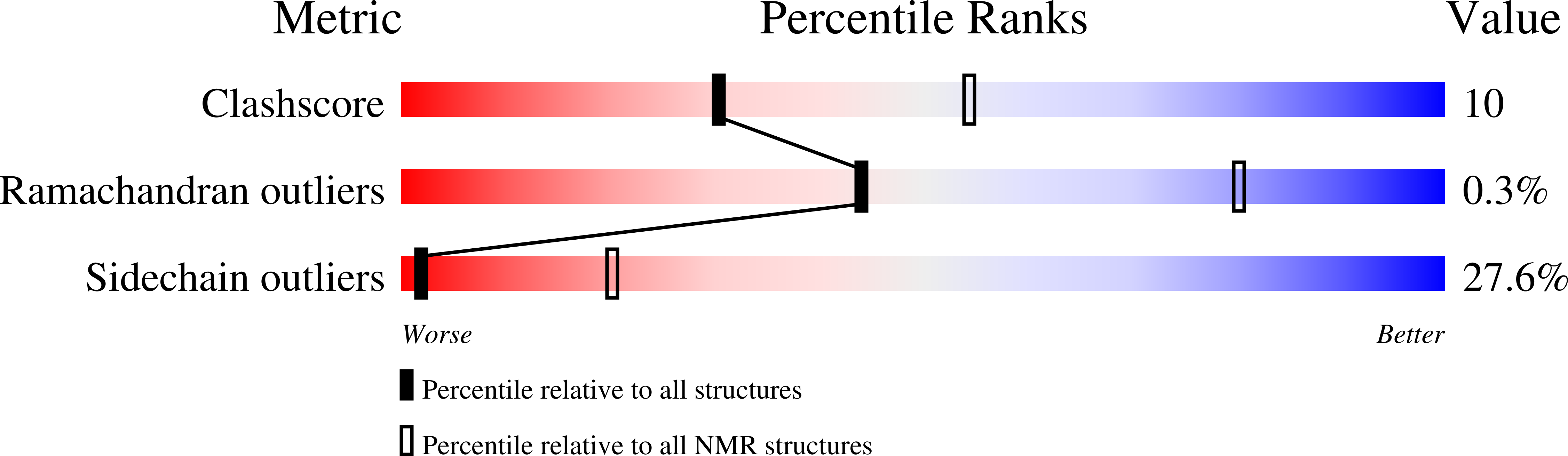The structural and functional effects of the familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy-linked cardiac troponin C mutation, L29Q.
Robertson, I.M., Sevrieva, I., Li, M.X., Irving, M., Sun, Y.B., Sykes, B.D.(2015) J Mol Cell Cardiol 87: 257-269
- PubMed: 26341255
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.08.017
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2N79 - PubMed Abstract:
Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (FHC) is characterized by severe abnormal cardiac muscle growth. The traditional view of disease progression in FHC is that an increase in the Ca(2+)-sensitivity of cardiac muscle contraction ultimately leads to pathogenic myocardial remodeling, though recent studies suggest this may be an oversimplification. For example, FHC may be developed through altered signaling that prevents downstream regulation of contraction. The mutation L29Q, found in the Ca(2+)-binding regulatory protein in heart muscle, cardiac troponin C (cTnC), has been linked to cardiac hypertrophy. However, reports on the functional effects of this mutation are conflicting, and our goal was to combine in vitro and in situ structural and functional data to elucidate its mechanism of action. We used nuclear magnetic resonance and circular dichroism to solve the structure and characterize the backbone dynamics and stability of the regulatory domain of cTnC with the L29Q mutation. The overall structure and dynamics of cTnC were unperturbed, although a slight rearrangement of site 1, an increase in backbone flexibility, and a small decrease in protein stability were observed. The structure and function of cTnC was also assessed in demembranated ventricular trabeculae using fluorescence for in situ structure. L29Q reduced the cooperativity of the Ca(2+)-dependent structural change in cTnC in trabeculae under basal conditions and abolished the effect of force-generating myosin cross-bridges on this structural change. These effects could contribute to the pathogenesis of this mutation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Randall Division of Cell & Molecular Biophysics, King's College London, London SE1 1UL, UK; British Heart Foundation Centre of Research Excellence, King's College London, London SE1 1UL, UK; Department of Biochemistry, Medical Sciences Building, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta T6G 2H7, Canada.