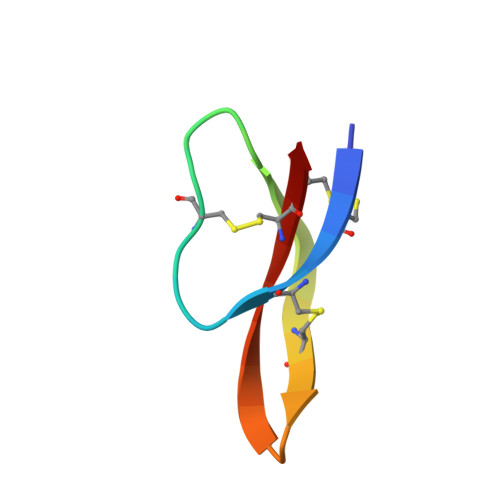
NMR solution structure and condition-dependent oligomerization of the antimicrobial Peptide human defensin 5.
Wommack, A.J., Robson, S.A., Wanniarachchi, Y.A., Wan, A., Turner, C.J., Wagner, G., Nolan, E.M.(2012) Biochemistry 51: 9624-9637
- PubMed: 23163963
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi301255u
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LXZ - PubMed Abstract:
Human defensin 5 (HD5) is a 32-residue host-defense peptide expressed in the gastrointestinal, reproductive, and urinary tracts that has antimicrobial activity. It exhibits six cysteine residues that are regiospecifically oxidized to form three disulfide bonds (Cys(3)-Cys(31), Cys(5)-Cys(20), and Cys(10)-Cys(30)) in the oxidized form (HD5(ox)). To probe the solution structure and oligomerization properties of HD5(ox), and select mutant peptides lacking one or more disulfide bonds, NMR solution studies and analytical ultracentrifugation experiments are reported in addition to in vitro peptide stability assays. The NMR solution structure of HD5(ox), solved at pH 4.0 in 90:10 H(2)O/D(2)O, is presented (PDB: 2LXZ ). Relaxation T(1)/T(2) measurements and the rotational correlation time (τ(c)) estimated from a (15)N-TRACT experiment demonstrate that HD5(ox) is dimeric under these experimental conditions. Exchange broadening of the Hα signals in the NMR spectra suggests that residues 19-21 (Val(19)-Cys(20)-Glu(21)) contribute to the dimer interface in solution. Exchange broadening is also observed for residues 7-14 comprising the loop. Sedimentation velocity and equilibrium studies conducted in buffered aqueous solution reveal that the oligomerization state of HD5(ox) is pH-dependent. Sedimentation coefficients of ca. 1.8 S and a molecular weight of 14 363 Da were determined for HD5(ox) at pH 7.0, supporting a tetrameric form ([HD5(ox)] ≥ 30 μM). At pH 2.0, a sedimentation coefficient of ca. 1.0 S and a molecular weight of 7079 Da, corresponding to a HD5(ox) dimer, were obtained. Millimolar concentrations of NaCl, CaCl(2), and MgCl(2) have a negligible effect on the HD5(ox) sedimentation coefficients in buffered aqueous solution at neutral pH. Removal of a single disulfide bond results in a loss of peptide fold and quaternary structure. These biophysical investigations highlight the dynamic and environmentally sensitive behavior of HD5(ox) in solution, and provide important insights into HD5(ox) structure/activity relationships and the requirements for antimicrobial action.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA.