Functional and Structural Characterization of Rsbu, a Stress Signaling Protein Phosphatase 2C
Delumeau, O., Dutta, S., Brigulla, M., Kuhnke, G., Hardwicku, S.W., Voelker, U., Yudkin, M.D., Lewis, R.J.(2004) J Biol Chem 279: 40927
- PubMed: 15263010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M405464200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1W53 - PubMed Abstract:
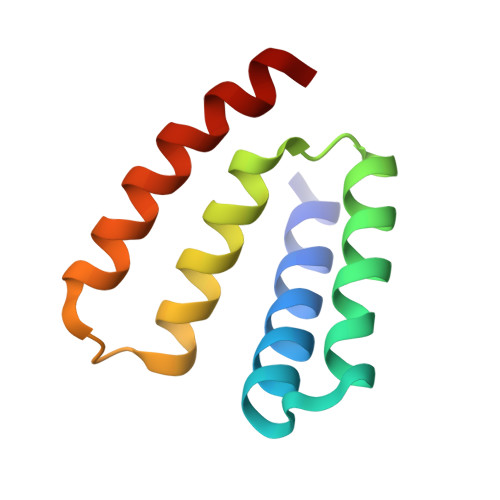
RsbU is a positive regulator of the activity of sigmaB, the general stress-response sigma factor of Gram+ microorganisms. The N-terminal domain of this protein has no significant sequence homology with proteins of known function, whereas the C-terminal domain is similar to the catalytic domains of PP2C-type phosphatases. The phosphatase activity of RsbU is stimulated greatly during the response to stress by associating with a kinase, RsbT. This association leads to the induction of sigmaB activity. Here we present data on the activation process and demonstrate in vivo that truncations in the N-terminal region of RsbU are deleterious for the activation of RsbU. This conclusion is supported by comparisons of the phosphatase activities of full-length and a truncated form of RsbU in vitro. Our determination of the crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of RsbU from Bacillus subtilis reveals structural similarities to the regulatory domains from ubiquitous protein phosphatases and a conserved domain of sigma-factors, illuminating the activation processes of phosphatases and the evolution of "partner switching." Finally, the molecular basis of kinase recruitment by the RsbU phosphatase is discussed by comparing RsbU sequences from bacteria that either possess or lack RsbT.
Organizational Affiliation:
Microbiology Unit and Laboratory of Molecular Biophysics, Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford, Oxford OX1 3QU, United Kingdom.