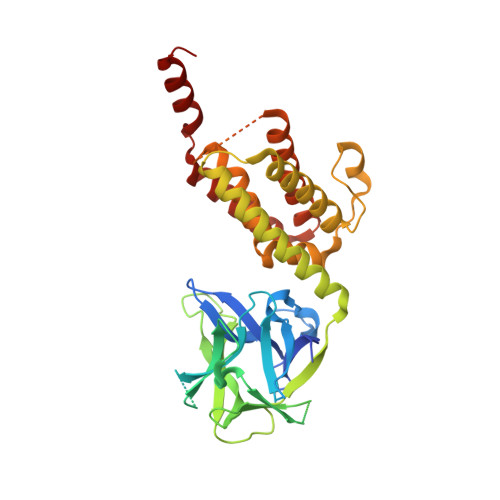
Structure of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor binding core in complex with its ligand.
Bosanac, I., Alattia, J.R., Mal, T.K., Chan, J., Talarico, S., Tong, F.K., Tong, K.I., Yoshikawa, F., Furuichi, T., Iwai, M., Michikawa, T., Mikoshiba, K., Ikura, M.(2002) Nature 420: 696-700
- PubMed: 12442173
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01268
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1N4K - PubMed Abstract:
In a variety of cells, the Ca2+ signalling process is mediated by the endoplasmic-reticulum-membrane-associated Ca2+ release channel, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) receptor (InsP3R). Being ubiquitous and present in organisms ranging from humans to Caenorhabditis elegans, InsP3R has a vital role in the control of cellular and physiological processes as diverse as cell division, cell proliferation, apoptosis, fertilization, development, behaviour, memory and learning. Mouse type I InsP3R (InsP3R1), found in high abundance in cerebellar Purkinje cells, is a polypeptide with three major functionally distinct regions: the amino-terminal InsP3-binding region, the central modulatory region and the carboxy-terminal channel region. Here we present a 2.2-A crystal structure of the InsP3-binding core of mouse InsP3R1 in complex with InsP3. The asymmetric, boomerang-like structure consists of an N-terminal beta-trefoil domain and a C-terminal alpha-helical domain containing an 'armadillo repeat'-like fold. The cleft formed by the two domains exposes a cluster of arginine and lysine residues that coordinate the three phosphoryl groups of InsP3. Putative Ca2+-binding sites are identified in two separate locations within the InsP3-binding core.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Molecular and Structural Biology, Ontario Cancer Institute and Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, 610 University Avenue, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5G 2M9.