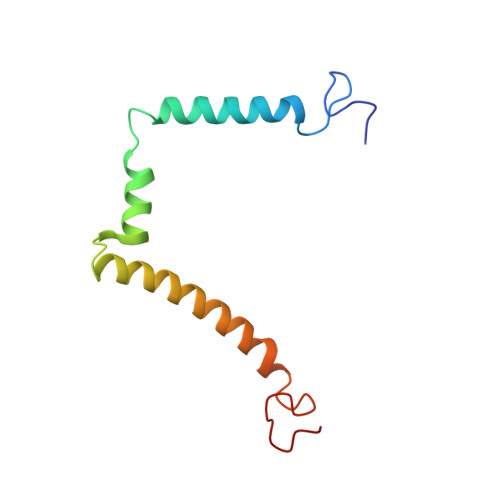
NMR structure of the HIV-1 regulatory protein Vpr in H2O/trifluoroethanol. Comparison with the Vpr N-terminal (1-51) and C-terminal (52-96) domains.
Wecker, K., Morellet, N., Bouaziz, S., Roques, B.P.(2002) Eur J Biochem 269: 3779-3788
- PubMed: 12153575
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03067.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ESX - PubMed Abstract:
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1, HIV-1, genome encodes a highly conserved regulatory gene product, Vpr (96 amino acids), which is incorporated into virions in quantities equivalent to those of the viral Gag protein. In infected cells, Vpr is believed to function during the early stages of HIV-1 replication (such as transcription of the proviral genome and migration of preintegration nuclear complex), blocks cells in G2 phase and triggers apoptosis. Vpr also plays a critical role in long-term AIDS disease by inducing viral infection in nondividing cells such as monocytes and macrophages. To gain deeper insight of the structure-function relationship of Vpr, the intact protein (residues 1-96) was synthesized. Its three-dimensional structure was analysed using circular dichroism and two-dimensional 1H- and 15N-NMR and refined by restrained molecular dynamics. In addition, 15N relaxation parameters (T1, T2) and heteronuclear 1H-15N NOEs were measured. The structure of the protein is characterized by a well-defined gamma turn(14-16)-alpha helix(17-33)-turn(34-36), followed by a alpha helix(40-48)-loop(49-54)-alpha helix(55-83) domain and ends with a very flexible C-terminal sequence. This structural determination of the whole intact Vpr molecule provide insights into the biological role played by this protein during the virus life cycle, as such amphipathic helices are believed to be involved in protein-lipid bilayers, protein-protein and/or protein-nucleic acid interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Département de Pharmacochimie Moléculaire et Structurale, INSERM U266 CNRS UMR 8600, UFR des Sciences Pharmaceutiques et Biologiques, Paris, France. wecker@pasteur.fr