Solution structure of the epsilon subunit of the F1-ATPase from Escherichia coli and interactions of this subunit with beta subunits in the complex.
Wilkens, S., Capaldi, R.A.(1998) J Biol Chem 273: 26645-26651
- PubMed: 9756905
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.41.26645
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1BSH, 1BSN - PubMed Abstract:
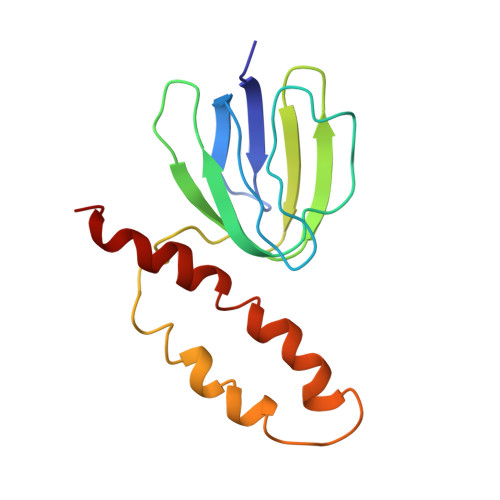
The solution structure of the epsilon subunit of the Escherichia coli F1-ATPase has been determined by NMR spectroscopy. This subunit has a two-domain structure with an N-terminal 10-stranded beta sandwich and a C-terminal antiparallel two alpha-helix hairpin, as described previously (Wilkens, S., Dahlquist, F. W., McIntosh, L. P., Donaldson, L. W., and Capaldi, R. A. (1995) Nat. Struct. Biol. 2, 961-967). New data show that the two domains interact in solution in an interface formed by beta strand 7 and the very C-terminal alpha-helix. This interface involves only hydrophobic interactions. The dynamics of the epsilon subunit in solution were examined. The two domains are relatively tightly associated with little or no flexibility relative to one another. The epsilon subunit can exist in two states in the ECF1F0 complex depending on whether ATP or ADP occupies catalytic sites. Proteolysis of the epsilon subunit in solution and when bound to the core F1 complex indicates that the conformation of the polypeptide in solution closely resembles the conformation of epsilon when bound to the F1 in the ADP state. Chemical and photo-cross-linking show that the epsilon subunit spans and interacts with two beta subunits in the ADP state. These interactions are disrupted on binding of ATP + Mg2+, as is the interaction between the N- and C-terminal domains of the epsilon subunit.
Organizational Affiliation:
University of Oregon, Institute of Molecular Biology, Eugene, Oregon 97403, USA.