NMR solution structure of the tandem Src homology 3 domains of p47phox complexed with a p22phox-derived proline-rich peptide
Ogura, K., Nobuhisa, I., Yuzawa, S., Takeya, R., Torikai, S., Saikawa, K., Sumimoto, H., Inagaki, F.(2006) J Biol Chem 281: 3660-3668
- PubMed: 16326715
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M505193200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WLP - PubMed Abstract:
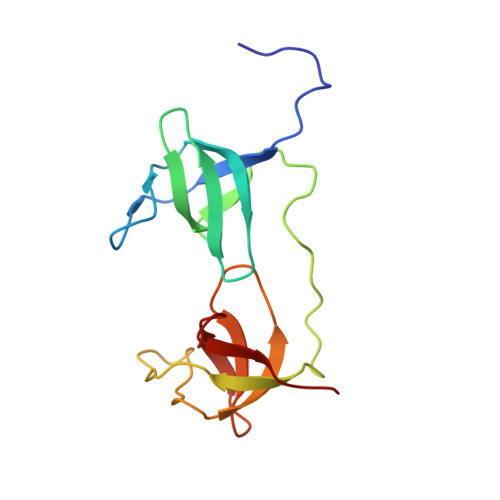
The phagocyte NADPH oxidase plays a crucial role in host defense against microbial infections by generating reactive oxygen species. It is a multisubunit enzyme composed of membrane-bound flavocytochrome b558 as well as cytosolic components, including p47phox, which is essential for assembly of the complex. When phagocytes are activated, the cytosolic components of the NADPH oxidase translocate to flavocytochrome b558 due to binding of the tandem Src homology 3 (SH3) domains of p47phox to a proline-rich region in p22phox, a subunit of flavocytochrome b558. Using NMR titration, we first identified the proline-rich region of p22phox that is essential for binding to the tandem SH3 domains of p47phox. We subsequently determined the solution structure of the p47phox tandem SH3 domains complexed with the proline-rich peptide of p22phox using NMR spectroscopy. In contrast to the intertwined dimer reported for the crystal state, the solution structure is a monomer. The central region of the p22phox peptide forms a polyproline type II helix that is sandwiched by the N- and C-terminal SH3 domains, as was observed in the crystal structure, whereas the C-terminal region of the peptide takes on a short alpha-helical conformation that provides an additional binding site with the N-terminal SH3 domain. Thus, the C-terminal alpha-helical region of the p22phox peptide increases the binding affinity for the tandem SH3 domains of p47phox more than 10-fold.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural Biology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Hokkaido University, N-12 W-6, Kita-ku, Sapporo 060-0812, Japan.