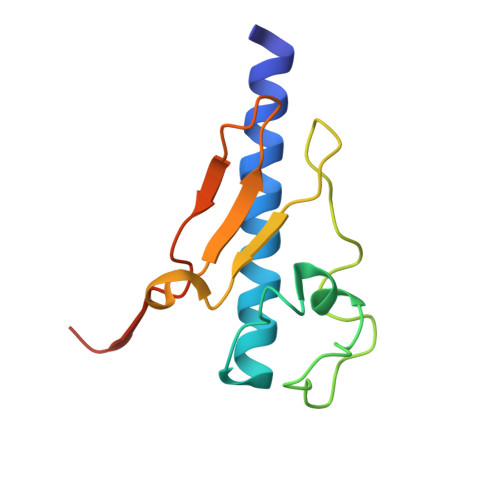
Structure and assembly of the pseudopilin PulG.
Koehler, R., Schaefer, K., Mueller, S., Vignon, G., Diederichs, K., Philippsen, A., Ringler, P., Pugsley, A.P., Engel, A., Welte, W.(2004) Mol Microbiol 54: 647-664
- PubMed: 15491357
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04307.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1T92 - PubMed Abstract:
The pseudopilin PulG is one of several essential components of the type II pullulanase secretion machinery (the Pul secreton) of the Gram-negative bacterium Klebsiella oxytoca. The sequence of the N-terminal 25 amino acids of the PulG precursor is hydrophobic and very similar to the corresponding region of type IV pilins. The structure of a truncated PulG (lacking the homologous region), as determined by X-ray crystallography, was found to include part of the long N-terminal alpha-helix and the four internal anti-parallel beta-strands that characterize type IV pilins, but PulG lacks the highly variable loop region with a disulphide bond that is found in the latter. When overproduced, PulG forms flexible pili whose structural features, as visualized by electron microscopy, are similar to those of bacterial type IV pili. The average helical repeat comprises 17 PulG subunits and four helical turns. Electron microscopy and molecular modelling show that PulG probably assembles into left-handed helical pili with the long N-terminal alpha-helix tightly packed in the centre of the pilus. As in the type IV pilins, the hydrophobic N-terminal part of the PulG alpha-helix is necessary for its assembly. Subtle sequence variations within this highly conserved segment seem to determine whether or not a type IV pilin can be assembled into pili by the Pul secreton.
Organizational Affiliation:
Molecular Genetics Unit, Institut Pasteur, 25, rue du Dr Roux, 75724 Paris Cedex 15, France.