Staggered molecular packing in crystals of a collagen-like peptide with a single charged pair.
Kramer, R.Z., Venugopal, M.G., Bella, J., Mayville, P., Brodsky, B., Berman, H.M.(2000) J Mol Biol 301: 1191-1205
- PubMed: 10966815
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.4017
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
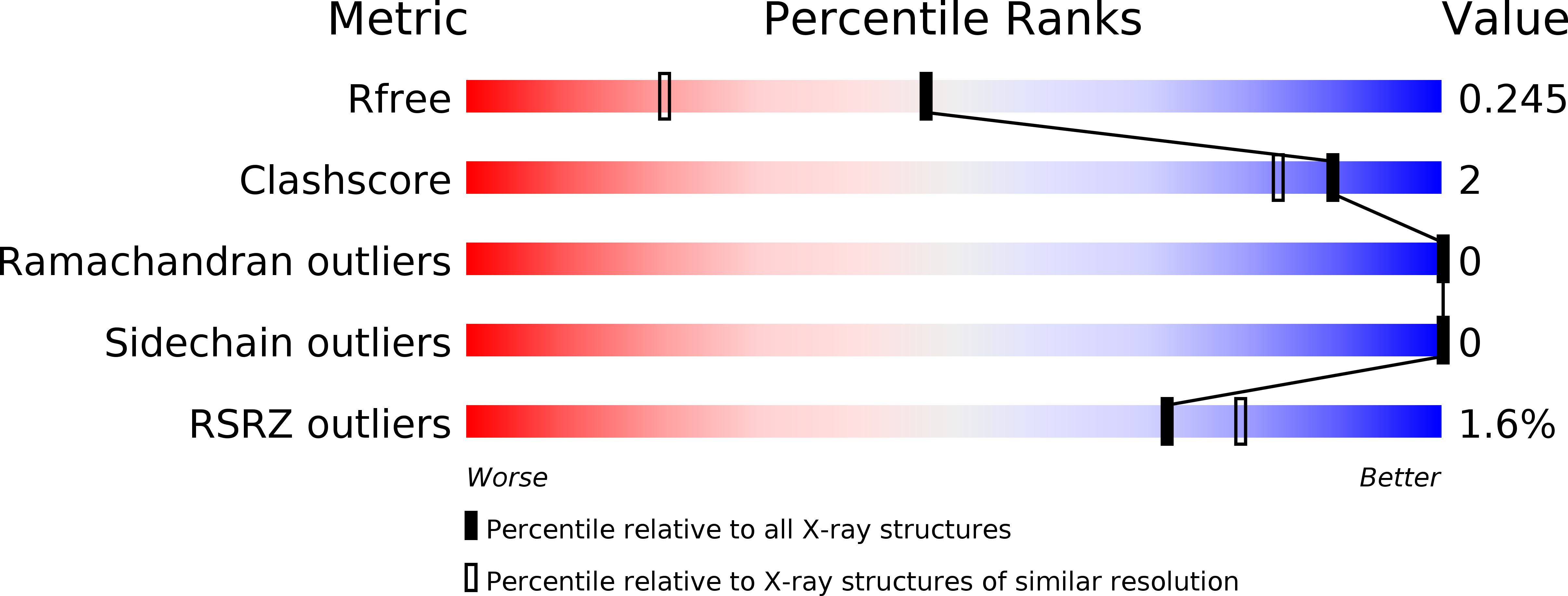
1QSU - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of the triple-helical peptide, (Pro-Hyp-Gly)(4)-Glu-Lys-Gly-(Pro-Hyp-Gly)(5) has been determined to 1.75 A resolution. This peptide was designed to examine the effect of a pair of adjacent, oppositely charged residues on collagen triple-helical conformation and intermolecular interactions. The molecular conformation (a 7(5) triple helix) and hydrogen bonding schemes are similar to those previously reported for collagen triple helices and provides a second instance of water mediated N--H . . . O==C interchain hydrogen bonds for the amide group of the residue following Gly. Although stereochemically capable of forming intramolecular or intermolecular ion pairs, the lysine and glutamic acid side-chains instead display direct interactions with carbonyl groups and hydroxyproline hydroxyl groups or interactions mediated by water molecules. Solution studies on the EKG peptide indicate stabilization at neutral pH values, where both Glu and Lys are ionized, but suggest that this occurs because of the effects of ionization on the individual residues, rather than ion pair formation. The EKG structure suggests a molecular mechanism for such stabilization through indirect hydrogen bonding. The molecular packing in the crystal includes an axial stagger between molecules, reminiscent of that observed in D-periodic collagen fibrils. The presence of a Glu-Lys-Gly triplet in the middle of the sequence appears to mediate this staggered molecular packing through its indirect water-mediated interactions with backbone C==O groups and side chains.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Rutgers University, 610 Taylor Rd, Piscataway, NJ, 08854-8087, USA.